Weird Extinct Animals: A Journey Through Time

Overview of the Topic
The world of extinct animals is as captivating as it is mysterious. Many of these creatures have left imprints on both our natural history and imagination. When one thinks of extinct animals, images of dinosaurs might come to mind, yet the true diversity encompasses a staggering range of bizarre and peculiar species that roamed the Earth long before humans ever set foot on it. Exploring these weird extinct animals not only ignites curiosity but also helps us understand the ecological narratives that framed our planet.
Definition of Key Terms
Before diving deeper, it’s essential to clarify some terms often discussed in the realm of extinct species.
- Extinction: Refers to the end of an organism or species, where no living individuals remain.
- Paleontology: The branch of science concerned with fossil animals and plants, providing insights into the past ecosystems.
- Ecosystem: A community of living organisms and their environment, interconnected in various roles.
These definitions lay the groundwork for understanding the rich tapestry of life that once existed and the lessons it offers us today.
Historical Significance
Historically, the extinction of animals has come about through various factors, natural and anthropogenic. Ice ages, volcanic eruptions, and climate changes played a vital part in shaping wildlife. However, the role humans have increasingly played in the last few thousand years has reshaped species landscapes dramatically.
Consider the Megalodon, a titan among sharks, known for its immense size and predatory skills. This apex predator dominated marine ecosystems before vanishing alongside the drastic environmental changes. Its extinction signifies how shifts in habitat and food sources can lead to a ripple effect impacting various forms of life:
"The loss of even a single species can trigger changes throughout an entire ecosystem."
This understanding prompts a deeper reflection on current biodiversity, prompting us to consider our modern-day responsibilities to the existing species that grace our planet.
As we delve into the characteristics and ecological roles of these bizarre animals, we begin to piece together clues of the past that enrich our understanding of today’s biodiversity. By identifying their unique traits and the ecosystems they inhabited, we can hint at broader evolutionary narratives and comprehend the broader implications of extinction.
Through this article, we will explore the world of these unusual extinct animals, drawing connections between their existence and the lessons they offer regarding conservation and ecological balance. The echoes of their past ripple into our present and future, urging rock and fossil collectors to consider what these ancient beings reveal about the world's intricate web of life.
Preface to Weird Extinct Animals
The natural world is teeming with diversity, which often leads to a concept of normalcy and an inherent preference for the familiar. However, this article aims to step aside from the pedestrian and delve into the realm of the peculiar—the weird extinct animals that once roamed our planet. Understanding these strange creatures not only offers insight into the animal kingdom but also taps into an evolutionary narrative filled with unexpected twists and turns. The importance of exploring weird extinct animals lies in their unique traits and behaviors that challenge our assumptions about nature and adaptation.
These eccentric species, with their outlandish characteristics, serve as a window into the past, revealing how life can flourish in dramatically different forms. By examining them, we help to unravel the complex history of life on Earth, including the mechanisms that govern survival and extinction. Furthermore, these creatures enrich our comprehension of past ecosystems and how biodiversity developed into what we see today.
To fully appreciate the significance of these weird beings, it’s essential to grasp the nuances of what constitutes 'weird' within the animal kingdom.
The Concept of 'Weird Within the Animal Kingdom'
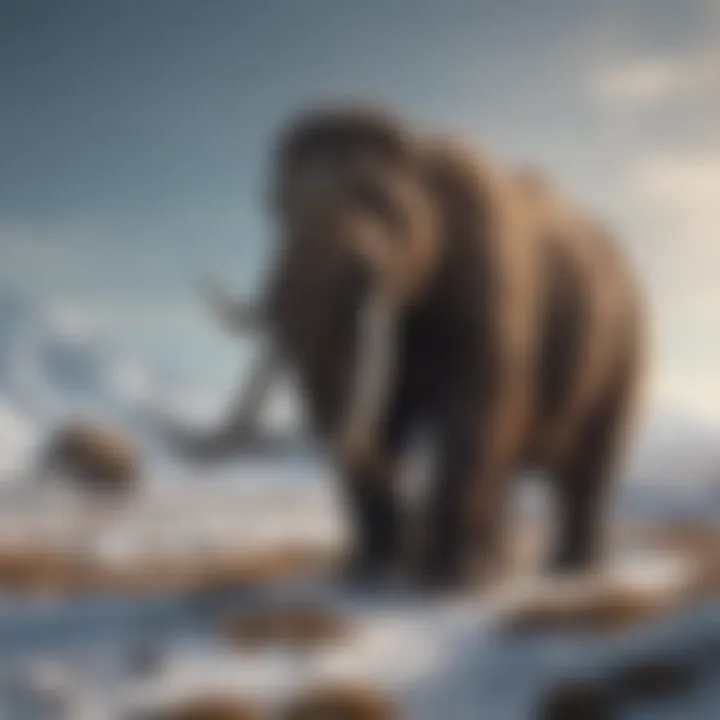
What exactly do we mean when we refer to an animal as weird? The term can stretch across various attributes—morphological oddities, behavioral quirks, or even unique ecological niches. For example, consider the woolly mammoth. While ostensibly resembling its modern relatives, the features of mammoths—such as their enormous tusks and thick fur adapted to cold climates—set them apart.
Other organisms, like the yet-to-be-discovered giant sea scorpion that existed hundreds of millions of years ago, raise the question of adaptability and environmental interaction. These examples underscore that 'weird' is often tied to context. In an evolutionary sense, what might seem peculiar today could have conferred significant advantages to those species in their respective ecosystems.
The Role of Extinction in Evolution
Extinction is frequently viewed as a stark end; however, it is also a fundamental component of evolution. Each loss carries with it the potential for new species to arise, filling the ecological gaps left behind. This cyclical dance of creation and destruction is crucial for maintaining biodiversity.
Consider the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event that wiped out the dinosaurs. In the wake of their demise, mammals—which were once underlings in the grand narrative—began to diversify and occupy niches previously unavailable to them. This phenomenon illustrates how extinction can pave the way for the emergence of magnificent variations, including those that may appear quirky or 'weird' to us today.
Thus, the need to understand these extinct oddities not only sheds light on the evolutionary pathways that led to them but also illustrates the broader consequences of extinction in shaping the world as we know it. The journey into the strange and often bizarre world of extinct animals is fundamental to appreciating biodiversity's intricate tapestry.
Framework for Understanding Extinction
Understanding the concept of extinction is vital when delving into the world of bizarre extinct animals. It lays the foundation for appreciating their historical contexts and the evolutionary dynamics that led to their peculiar traits. Getting a grip on extinction helps in grasping the larger narrative of how life has evolved on Earth, shudders through hardship, and often creates new forms in the wake of environmental changes.
At its core, the framework for understanding extinction revolves around comprehending what extinction truly means within biological contexts. It’s more than just the end of a species; it's a complex interplay of evolutionary forces, environmental shifts, and ecological balance. This knowledge provides insight into not just the creatures that are no longer with us, but also how their absence continues to reverberate through ecosystems today.
Defining Extinction: A Biological Perspective
From a biological standpoint, extinction marks the complete disappearance of a species from Earth. The World Wildlife Fund has noted that in recent centuries, human activities have accelerated this process. This has left significant impacts on biodiversity.
There are two primary types of extinction:


- Background Extinction: A natural, gradual process where species die off at a regular pace due to various factors including predation, competition, and environmental changes.
- Mass Extinction: Characterized by a sudden loss of a vast number of species in a relatively short time. Historical records identify five major mass extinction events, where biodiverse havens fell silent.
The study of these extinction processes paints a clearer picture of how species adapt—or fail to do so. Several factors contribute to extinction: habitat loss, climate influence, disease outbreaks, and invasive species among others. Understanding these elements gives researchers keys to unlock the reasons behind many bizarre adaptations seen in extinct creatures.
Major Extinction Events
Reflecting on the major extinction events throughout Earth’s history shines a light on the tumultuous journey of life:
- Ordovician-Silurian Extinction: Approximately 440 million years ago, this event wiped out about 85% of marine species. It was triggered by a severe ice age.
- Late Devonian Extinction: Taking place over several million years, this extinction event saw roughly 75% of species vanish, likely due to climate changes and ocean anoxia.
- Permian-Triassic Extinction: Known as the Great Death, it occurred about 252 million years ago, with an estimated 90% of species going extinct. Volcanic activity and climate instability played significant roles.
- Triassic-Jurassic Extinction: Marking the transition to the age of dinosaurs, this event eradicated about 50% of species, again due to climate shifts and volcanic eruptions.
- Cretaceous-Paleogene Extinction: Most famously known for ending the dinosaurs around 66 million years ago, this extinction was caused by a combination of asteroid impact and relentless volcanic activity.
"Studying these events helps us understand not just what existed, but why certain animals developed unique adaptations that were often their undoing."
The lessons drawn from these extinction events are numerous and deeply relevant today. They hold a mirror to current biodiversity issues, where human actions echo past patterns leading to rapid declines in various species, raising eyebrows and concerns in conservation circles.
In summary, engaging with the framework of extinction provides an essential backdrop to understand the unique and fascinating creatures that once roamed the Earth. By analyzing the biological definitions and historical precedents of extinction, readers can appreciate the interconnected tapestry of life and loss throughout time.
Types of Weird Extinct Animals
The exploration of weird extinct animals offers a fascinating insight into the diversity and oddities that once roamed our planet. Understanding the various types of these creatures allows us to appreciate their roles within their ecosystems and recognize the factors that led to their extinction. Each category highlights unique traits that provide clarity on how different species adapted to their environments and influenced their surroundings. By examining this subject, we can learn about the intricacies of life in prehistoric times and the ecological balance that existed before the adaptations of the present-day animals began.
Megafauna and Their Unusual Traits
Examples of Megafauna
Megafauna refers to large animals, typically over 100 pounds, that emerged during various periods, notably the Pleistocene epoch. These beings often sported unconventional characteristics. One such example is the Megalodon, an enormous prehistoric shark that could reach lengths of up to 60 feet. This sea beast reveals much about the dynamics of ancient oceans, as its presence would have profoundly impacted marine food chains.
What makes Megafauna like the woolly mammoth particularly compelling is their adaptation to cold climates. These animals developed thick fur, a layer of fat, and even long tusks for foraging, illustrating how environmental challenges shape living beings. Studying these traits gives us a glimpse into the harsh realities of survival and the methods employed by these colossal creatures to thrive.
Ecological Impact of Megafauna
The ecological impact of Megafauna is crucial to understanding historical ecosystems. These large animals played a significant role in shaping their environments. For instance, the giant ground sloth not only altered vegetation but also helped disperse seeds, contributing to diverse flora. In areas where large herbivores thrived, their grazing habits helped maintain grassland ecosystems and create habitats for various species.
Their extinction had significant repercussions. With these creatures no longer roaming the earth, many ecosystems suffered. The balance was disrupted, leading to overgrown vegetation and ultimately affecting the smaller species that depended on the habitats shaped by Megafauna. By investigating how these giants influenced their surroundings, we can draw wild parallels to the importance of biodiversity in today's world.
Uncommon Marine Species
Unique Adaptations
The uniqueness of certain extinct marine species stands out due to their strange adaptations, which often seem more suited for science fiction than reality. Take, for instance, the dunkleosteus, a prehistoric fish that had armored plates and could slice through prey with its jaw, which was not equipped with teeth in the traditional sense but rather sharp beak-like structures. This unique feature helped it navigate its harsh aquatic environment and secure its place as a formidable predator.
Such adaptations not only make these species unique but also highlight how life can evolve remarkably in response to specific ecological pressures. By studying these adaptations, we gain insight into evolutionary processes, survival mechanisms, and how the marine environment has changed over time.
Fossil Evidence
Fossil evidence is vital for understanding extinct marine species. Fossils provide tangible proof of these organisms and their adaptations, and they describe vital details of their habitats and environments through stratigraphy. The discovery of fossilized remains of the Ichthyosaur, resembling a streamlined dolphin, showcases an evolutionary experiment where reptiles adapted to life in the ocean.
The fossil record serves not only as a historical ledger but also helps scientists decipher past climatic conditions. Fossils can illustrate shifts in environments over time, revealing how species migrated and adapted to changing seas. Recognizing these patterns can enhance current conservation practices by showing trends in biodiversity and ecosystem changes.
Strange Terrestrial Creatures
Adaptations to Environments
Strange terrestrial creatures represent some of the most bizarre and fascinating adaptations in nature. For example, the thylacine, also known as the Tasmanian tiger, had a unique mix of traits that looked strikingly like a dog despite being a marsupial. Its adaptations to a nocturnal lifestyle and its hunting techniques highlight how versatile life can be in various habitats.
Understanding these adaptations gives us clues about resource utilization and how animals interact with their environments. It underscores the importance of environmental factors in shaping behavioral patterns and physical traits.
Symbiotic Relationships
Exploring symbiotic relationships among extinct creatures unveils a complex web of interactions that aided survival and ecological balance. One fascinating example is the Pleistocene giant tortoise, which was likely part of a mutualistic relationship with various plant species, helping to disperse seeds through its movements across landscapes.
This interdependence underscores the fine dance of ecosystems. When one partner goes extinct, the other often struggles to adapt. By examining these relationships, we unlock a deeper appreciation of how interconnected life forms truly are and the repercussions that follow when a single link in that chain is lost.


The study of weird extinct animals is not just a scientific endeavor; it’s a window into the evolutionary narrative that has shaped life on Earth.
Fascinating Features of the Extinct
Understanding the peculiar traits of extinct animals serves as a window into the dynamic processes that have shaped Earth's biodiversity. The features of these lost species reveal not only their adaptations but also the evolutionary experiments that nature undertook over millions of years. By examining these fascinating features, we can draw connections to present-day biodiversity, enrich our knowledge of ecology, and even find parallels in modern species.
Morphological Oddities
Morphological oddities refer to the unusual physical characteristics that set certain extinct animals apart from their contemporaries or living relatives. These unique forms often come with intriguing stories behind their evolution and existence.
Consider the iconic woolly mammoth, with its massive tusks and long, shaggy coat. Adapted to the icy tundras of the Pleistocene era, its unique features not only helped it survive harsh conditions, but they also paint a vivid picture of an environment that has drastically changed. The mammoth's body was insulated with a thick layer of fat, while its large ears minimized heat loss, making it a stunning example of how morphology adapts to climate.
Another bizarre creature to note is the Entelodon, often referred to as the "terminator pig." Despite its swine-like appearance, species like these could reach over six feet in height and had the jaw strength to crush bone. This peculiar morphology reflects the predator-prey dynamics of its time and offers insight into what niche these animals filled in their ecosystems.
From armor-like skin of the Ankylosaurus to the long necks of the Sauropods, each feature resonates with adaptations that were essential for survival in their specific habitats. These adaptations also fostered various ecological interactions, showcasing how morphology plays a crucial role in the web of life.
Behavioral Anomalies
Beyond their physical attributes, extinct animals exhibited behavioral anomalies that reveal the complexity of their lives and interactions. These behaviors often manifest in various ways, from their feeding habits to social structures and reproductive strategies.
Take the Dodo, for example. This flightless bird, once a common sight on the island of Mauritius, displayed a distinct lack of fear towards humans, likely due to the absence of predators on its home turf. This behavioral trait became its undoing after the arrival of sailors, leading to its extinction in the late 17th century. Its story serves as a cautionary tale about the vulnerability of isolated ecosystems.
Then there's the fascinating case of Megalania, a giant monitor lizard from Australia. Evidence suggests that it might have employed ambush tactics to hunt, showcasing a level of predatory behavior similar to that of modern crocodiles. Such insights into the behavioral patterns of past species can inform our understanding of how behaviors evolve over time, often in response to environmental pressures.
"These distinct traits and behaviors tell us more than just 'what' these creatures were; they provide glimpses into 'how' they lived and interacted with their ecosystems."
The Impact of Extinction on Biodiversity
The concept of extinction is not just about loss; it deeply intertwines with the narrative of biodiversity on our planet. Understanding the impact of extinction on biodiversity serves as a crucial key to unlocking the mysteries of our past ecosystems while shedding light on current environmental challenges. Extinction sets off a chain reaction that can significantly reshape ecosystems, influencing everything from food webs to population dynamics. An appreciation of this topic offers insights into how diverse life forms have shaped and continue to shape the world around us.
Lessons from Past Extinctions
Past extinction events have left profound marks across the globe, and these lessons highlight the relatively fragile balance of ecosystems. The Permian-Triassic extinction, for instance, is known as the Great Dying, where about 90% of marine species vanished. This event teaches us about resilience; the recovery saw new species emerge that fit the existing ecological niches. In particular, the rise of dinosaurs after their own extinction bi-levels offers a look into how life can adapt and fill voids left behind.
- Ecosystem recovery: Post-extinction environments can lead to bursts of evolutionary innovation, providing fresh opportunities for adaptation among surviving species.
- Niche competition: As some species fade away, others can expand their habitats or behaviors, leading to the development of new species adapted to available niches.
Statistics from paleontological research illustrate that biodiversity can rebound after mass extinction events, often resulting in a wider variety of life forms. This resilience is essential to reminding us how ecosystems can reorganize and recover despite seeming overwhelming odds.
Repercussions for Current Ecosystems
Fast forward to the present, the repercussions of historical extinction events carry weight, especially as humanity faces its own biodiversity crisis. Today’s extinctions—often driven by factors like habitat destruction, climate change, and pollution—mirror past patterns but at an accelerated pace.
Current ecosystems exhibit pressures that echo those of the past, as a multitude of species vanish. This raises alarms about the long-term viability of ecosystems. In particular:
- Loss of Keystone Species: Some species play crucial roles in their ecosystems. Their loss leads to unpredictable outcomes, such as the decline of certain plants or the collapse of food sources for other animals.
- Altered Interactions: The relationships between species can become unbalanced, resulting in invasive species taking over, thus further decreasing overall biodiversity.
"The extinction of a single species can tip the scales of a whole ecosystem, leading to cascading effects that fundamentally change its structure."
Paleontological studies underline that today’s losses could lead to future ecosystems that are vastly different from what we currently recognize. The understanding gained from extinct species informs conservation efforts, steering modern policies toward preserving what remains, as every missing link in an ecosystem can dampen future resilience.
In essence, the impact of extinction on biodiversity is a dynamic story of loss and adaptation, a narrative that urges us to act, to learn, and to conserve. Each extinct species carries lessons, not only about the past but about the future of all life on Earth.
Modern Insights from Extinct Species
Understanding extinct species is not just an exercise in pondering the past; it opens a window into the complex tapestry of life that once thrived on our planet. In fact, the study of these oddball creatures offers valuable lessons that inform not only paleontology but also contemporary conservation efforts and ecological strategies. The intricacies of their existence, adaptations, and eventual demise provide context to the evolution of modern biodiversity. The success and failure of these species play a pivotal role in shaping our current ecological landscape.
Research Techniques in Paleontology
Research in paleontology has evolved tremendously, especially with the advent of modern technology. Today, scientists delve into the past using a variety of techniques that enhance our understanding of extinct species.
- Radiometric Dating: This method allows researchers to accurately determine the age of fossils, providing chronological context to their existence.
- CT Scanning: By using advanced imaging techniques, paleontologists can visualize the intricate internal structures of fossils without causing damage. This opens up a treasure trove of information about morphology and functional adaptations.
- DNA Analysis: Despite the degradation of genetic material over time, advancements in extracting ancient DNA have led to surprising discoveries. For example, scientists have sequenced DNA from mammoths, giving us clues about their adaptations and evolutionary relationships with modern elephants.
- Field Excavations: Hands-on digging at paleontological sites remains fundamental. Each layer of sediment can reveal new fossils, giving context to biodiversity during different geological periods.


These techniques underscore a collaborative approach, integrating knowledge from various scientific disciplines—geology, biology, and even chemistry—to create a robust framework for understanding extinct species.
Fossil Discoveries and Their Importance
Fossils, often viewed as mere rock, are windows into epochs long gone. They tell us not just about the organisms themselves but also about the habitats they occupied and the environmental conditions of their time. Here’s why fossil discoveries are so crucial for understanding weird extinct animals:
- Reconstruction of Ancient Ecosystems: Fossils provide insights into past climates and habitats, allowing scientists to reconstruct ecosystems and understand how extinct species interacted with their environment.
- Insights into Evolution and Adaptation: By studying the morphology of various fossils, researchers can trace evolutionary changes and how certain traits emerged in response to environmental pressures.
- Identification of Extinction Patterns: Fossil records help in understanding the causes behind mass extinctions—be it climatic changes, asteroid impacts, or human interference—and the impacts of these events on biodiversity.
- Cultural and Educational Value: Fossils captivate the imagination of the public, bridging the gap between science and everyday life. Exhibitions in museums and educational programs foster a deeper understanding and appreciation of the natural world.
"Fossils are a record of life. They tell stories of survival and extinction that are crucial to understanding our own place in the natural world."
In essence, the importance of extinct animal studies lies in their ability to deepen our understanding of life’s resilience and adaptability, drawing important parallels with current ecosystems facing threats from human activities. The ongoing research continues to shape our knowledge and inform strategies for preservation, making the insights from extinct species not just historical curiosities, but vital components of modern conservation narratives.
The Cultural Significance of Extinct Animals
Examining the reverberating echoes of weird extinct animals goes beyond mere biological interest. These creatures have staked their claim in our collective culture, shaping how we perceive the past and informing our understanding of today’s biodiversity. The cultural significance of these oddities lies in their ability to capture imagination and provoke thought, leading to stories and teachings that span generations.
One of the key elements of this significance is how extinct animals have influenced art, literature, and culture at large. They serve as symbols of lost worlds, generating artistic expressions from illustrations to novels, where their peculiarities inspire creativity and contemplation about existence. As humans grapple with their fascination for the bizarre, these animals assume roles that challenge social narratives and evoke emotions, reminding us of life’s fragility.
Additionally, the insight these creatures provide into our ecological history is invaluable. The extinction of species often serves as a cautionary tale about our environmental responsibilities, pushing us to reflect on mankind's impact on other forms of life. When we study these weird beasts, we can draw parallels to current conservation efforts, fostering a deeper appreciation for the animals that still roam our Earth.
"The stories we tell about extinct animals not only reflect our curiosity about the past but also guide our actions for the future."
Influence on Art and Literature
The haunting allure of weird extinct animals has been a treasure trove for artists and writers throughout history. These unique beings, from the woolly mammoth to the dodo bird, have inspired countless creations, transcending simple representation into profound explorations of life, loss, and evolution.
In art, these creatures have often been depicted in dazzling ways, celebrating their odd traits. Paleontologists often collaborate with artists to animate lifelike renditions of these beings, capturing their essence and transporting viewers to ecological eras long gone. Such artworks not only serve educational purposes but also challenge perceptions, inviting people into a dialogue about the natural world.
Within literature, the narratives involving extinct animals are rife with symbolism. Various authors have utilized these creatures to explore themes of extinction, nostalgia, and the inevitability of change. For example, in The Last dodo, writers articulate humor tinged with melancholy, serving to educate readers while engaging their imaginations.
The creative reimagining of these species illustrates how cultural production evolves alongside scientific discoveries. As new fossils are uncovered, the narratives shift, broadening the tapestry of human understanding and cultural expression. This fluidity between science and art illustrates the importance of curiosity and striving to comprehend worlds unfathomable yet engaging.
Public Perception and Education
The cultural significance of extinct animals also manifests through public perception and education initiatives. Museums, documentaries, and media productions play crucial roles in shaping knowledge around these otherworldly creatures. Through engaging exhibits and interactive displays, educational institutions endeavor to inspire interest and a desire to learn more about paleontology and extinction.
Public perception often hinges on how these animals are framed within societal conversations about biodiversity and conservation. The marvelous existence of these species stirs a sense of wonder but can also elicit fear regarding the current ecological crisis. As society grapples with issues like climate change, extinction narratives prompt reflection and action.
Environmental education programs leverage the stories of bizarre extinct species to cultivate stewardship of the planet. They capitalize on our natural curiosity, transforming it into advocacy for current endangered animals. By weaving extinct animals into educational material, students are not only learning about the past but also about their role in the future of biodiversity.
In summary, the oddities of extinct animals have profoundly influenced culture and education, nurturing curiosity, consciousness, and care within society. Through stories, art, and education, they remain a reminder of our responsibility towards the living world, prompting us to learn from yesterday in order to navigate the complexities of tomorrow.
Ending: Reflecting on Weird Extinct Animals
Understanding weird extinct animals is like peeking behind the curtain of time. These creatures, with their peculiar features and unique adaptations, offer a glimpse into the diverse tapestry of life that once thrived on our planet. They remind us of nature’s vast creativity and the intricate web of relationships that defined ancient ecosystems.
The exploration of these oddities doesn't just enrich our knowledge of paleontology but also underscores the importance of biodiversity. Learning about the characteristics and roles of these extinct species can shed light on what may come next in our evolutionary story. After all, extinction is not just a monument of the past; it shapes the environment for those species that remain.
Continuing the Exploration of the Past
As we scratch the surface of ancient remains and fossils, the journey into the depths of our planet's history continues. Each fossil we unearth opens a window to understanding not just the animals that once roamed, swam, or flew, but also the climate and environment of their time. For rock and fossil collectors, these remnants serve as tangible connections to an exceedingly rich and diverse past.
Here are a few ways continued exploration can be pursued:
- Field Studies: Enthusiasts not only dig through the earth with shovels but also utilize cutting-edge technology like drones and LIDAR to map excavation sites.
- Collaboration with Academics: Joining forces with paleontologists and universities can yield significant insights, transforming hobbyists into contributors to science.
- Participating in Citizen Science: Engaging in local conservation efforts or fossil identifications helps build a community focused on preservation and education, bringing awareness to the importance of extinct animals.
Keeping the torch of curiosity alive is paramount; every fragment of bone or tusk tells a story waiting to be interpreted. As we uncover more, we might not only define extinct life more clearly but also draw connections to current species, analyzing how they adapt and change over time.
The Future of Paleontological Research
The field of paleontology is rapidly evolving, propelled by advancements in technology and methodologies. The road ahead promises exciting discoveries that could reshape our understanding of life on Earth and its extinction processes. For those invested in this realm, the future opens a slew of possibilities.
Consider these trends shaping the horizon of paleontological research:
- Genetic Analysis: With advancements in DNA extraction from fossils, researchers are beginning to understand the genetics of extinct species, providing information about their behaviors and relationships with current animals.
- High-Resolution Imaging Techniques: Techniques such as micro-CT scanning allow for detailed studies of fossils without damaging them, leading to more accurate representations of these creatures in research.
- Climate Modeling: As climate change remains a pressing concern, studies linking ancient extinction events with climatic shifts can inform current environmental strategies, enhancing our ability to anticipate future challenges.
Moreover, interdisciplinary approaches combining geology, biology, and technology can yield a more comprehensive view of past life forms, informing not only academic knowledge but also practical applications for conservation efforts today.















