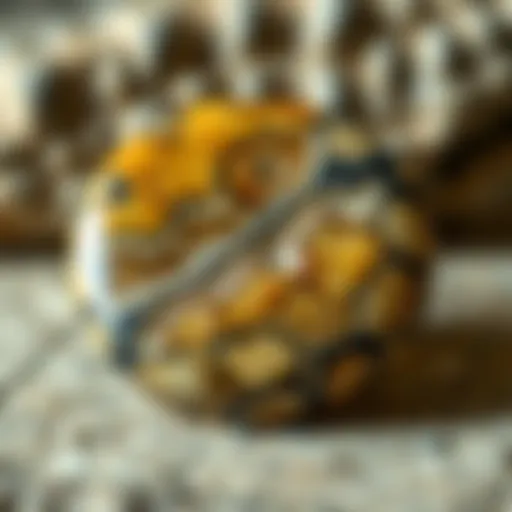
The Intriguing Value of Fluorite in Modern Industry


Intro
Fluorite, often called the "gem of the miners," captivates both the novice and seasoned rock collector alike. Its striking colors and impressive clarity make it a standout piece in collections around the globe. Beyond its visual allure, fluorite possesses a rich geochemical narrative and diverse applications—be it in industrial realms or the burgeoning collectibles market.
Understanding fluorite's value is about more than just the final price tag slapped on a piece. It encompasses a multitude of factors, from geological properties to ethical mining practices. For collectors, it’s essential to grasp the nuances of what elevates one specimen over another.
As we delve deeper into this captivating mineral, we’ll unravel its journey from the depths of the Earth to prized displays in collectors' cabinets.
Prologue to Fluorite's Value
Fluorite, often overshadowed by more popular minerals, deserves its moment in the spotlight. This colorful mineral, made up primarily of calcium fluoride, has captured the interest of both scientists and collectors alike. The importance of examining fluorite's value lies not just in its aesthetic appeal but also in its numerous applications and economic significance.
Understanding the value of fluorite provides insights into several areas, including geology, market trends, and sustainability. For enthusiasts, the various hues of fluorite, ranging from vibrant greens to deep purples, tell more than just a pretty story; they offer a glimpse into the conditions under which the mineral formed. Recognizing these aspects contributes to a deeper appreciation of this mineral and its role in the natural world.
Furthermore, fluorite's industrial applications cannot be overlooked. It is a vital component in the production of aluminum, gasoline, and even toothpaste. As industries evolve, capturing the nuances of fluorite's market dynamics becomes essential for both consumers and investors alike. A collector might find a piece that shines in more than one way – it can serve as both a decorative item and a potential investment.
Key points to consider when delving into fluorite’s value include:
- Geological Significance: Understanding its formation aids collectors in identifying and valuing specimens.
- Market Trends: Awareness of how demand fluctuates based on color, clarity, and rarity can lead to savvy purchasing decisions.
- Ethical Mining: As the conversation around sustainability grows, knowing the sources of fluorite becomes increasingly important.
"Fluorite is not just a gemstone; it's a window to the Earth’s history and a reflection of its ongoing story."
As we navigate through the intricate layers of fluorite’s worth, it becomes clear that this mineral is much more than a simple specimen. Its presence in both the natural and industrial worlds underscores a multifaceted value that extends beyond the physical, prompting a broader examination of how we interact with our planet. Thus, exploring fluorite's value sets the stage for a comprehensive understanding of its relevance across various contexts.
Understanding Fluorite: A Geological Perspective
Fluorite, a mineral that captivates both miners and collectors alike, is often overlooked in discussions about geological importance. Yet, understanding the geology of fluorite sheds light on not just its formation but also its myriad uses and economic value. This section seeks to enlighten the reader on the fundamental aspects related to fluorite's composition and structure, which directly influence its valuation in both geological and commercial fields.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Fluorite is primarily composed of calcium fluoride (CaF₂), a compound that brings about its striking characteristics. This simplicity belies the significance of its composition. Calcium fluoride crystalizes in the isometric system, leading to the formation of the octahedral crystals that are characteristic of fluorite.
This mineral is celebrated for its vibrant colors, ranging from deep purples and greens to less common shades like blue and even colorless forms. These variations often imply certain impurities; for instance, exposure to radiation can turn fluorite green, while the presence of certain minerals can create alluring hues.
In addition to its aesthetic properties, fluorite’s low melting point makes it useful in metallurgy. It acts as a flux, facilitating the fusion of metals and lowering the melting temperature required in smelting processes.
Crystal Structure and Varieties
Fluorite showcases an intriguing crystal structure that contributes to its popularity among rock and mineral collectors. The cubic arrangement not only allows for well-formed crystals but also leads to distinctive cleavage patterns, which can aid in identifying authentic samples.
Among the various types of fluorite, several noteworthy varieties stand out:
- Green Fluorite: Often associated with healing properties and the ability to enhance concentration.
- Purple Fluorite: This variety symbolizes wisdom and is said to calm the mind, which makes it a prized possession for collectors who are drawn to its deep hues.
- Blue Fluorite: Rare and exceptionally lovely, blue fluorite is often sought after for its unique coloration.
Collectors delight in specimens that display the fluorescence effect—exhibiting a glow under UV light. This quality adds another layer of intrigue, making fluorite not just a rock but a beautiful light show when displayed in the right conditions.
Moreover, some fluorite specimens host inclusions or unique formations, like phantom crystals, that tell a story of their geological journey. These elements can greatly affect value and desirability in the collector market.
"The value of a mineral lies not just in its physical properties but in the stories it carries—stories of time, pressure, and the unique conditions of its environment."
Understanding the geological perspective of fluorite not only enriches one's appreciation of this mineral but also paints a comprehensive picture of its role within market dynamics. Delving into the chemistry and structural varieties of fluorite sets the stage for further exploration into how these elements influence its placement in the market and its importance in industrial applications.


Factors Influencing Fluorite Value
Understanding what drives the value of fluorite goes beyond surface-level analysis. It's an intricate tapestry of variables that coalesce to determine how much collectors and industry professionals are willing to pay for this fascinating mineral. Factors like color, clarity, and rarity create an environment that shapes market trends and establishes a foundation for pricing. In this section, we will explore these facets, providing insights that help illuminate the broader implications of fluorite's value and its appeal, specifically to rock and fossil collectors.
Color Variations and Their Impact
Color is one of the most striking characteristics of fluorite, with variations ranging from vibrant greens, purples, blues, to even clear forms. Each hue can carry a different value. For instance, deep purple fluorite is often deemed more valuable than lighter shades due to its rarity in natural deposits. There are truly some breathtaking colors, and many collectors seek specific shades that resonate with them on a personal level.
"The allure of fluorite isn’t just in its beauty, but how that beauty gets interpreted in terms of value. Each color variation tells a different story about its geological journey."
Additionally, environmental factors—such as the presence of other minerals during formation—can affect the final color of a crystal. This not only adds to the gemstone's uniqueness but also raises its market demand among avid collectors and gem enthusiasts alike.
Clarity and Cuts: A Closer Look
When it comes to the visual appeal of fluorite, clarity plays a crucial role. The transparency of a specimen affects its aesthetic and, consequently, its value. Stones with minimal inclusions or imperfections tend to attract higher price tags, while those with noticeable flaws might languish on shelves. The beauty of a perfectly clear crystal often makes it a focal point in any collection.
Cuts can also greatly influence value. For example, well-executed faceting can enhance the brilliance of a fluorite specimen, making it more attractive to potential buyers.
Here are some points to consider about cuts and clarity:
- Brilliance: Brightness and light dispersion are better in well-cut stones.
- Shape: Different shapes (e.g., octagonal, rounded) can evoke different levels of desirability.
- Sizing: Larger, clearer pieces are rarer and often command higher prices.
Rarity and Availability in the Market
Rarity combined with availability makes for a volatile pricing environment. Fluorite is not uniformly available worldwide; certain regions yield specific colors and qualities more so than others. For instance, exceptionally clear and deep blue fluorite can be hard to find, making pieces from locations such as China or Mexico something of a collector's prize.
Demand fluctuates, influenced by emerging trends in both the collectibles market and industrial applications. When a particular color or clarity gains popularity, prices can skyrocket overnight, leaving less reputable specimens neglected. The challenge for collectors lies in recognizing these patterns without being swept away by trends.
Market Trends and Pricing Dynamics
Market trends and pricing dynamics play a pivotal role in understanding the economic significance of fluorite. Analyzing these elements not only gives insight into the present conditions of the fluorite market but also sheds light on its future potential—essential for both collectors and investors alike. As demand fluctuates based on industrial and decorative applications, pricing can vary considerably, creating a landscape filled with opportunities and risks. When discussing fluorite values, it is crucial to examine factors like supply chain effects, geopolitical influences, and changing consumer preferences.
Current Market Analysis
Presently, the fluorite market shows a robust demand mainly due to its applications in various industries. As industries continue to expand—such as ceramics and metallurgy—the reliance on fluorite for its unique properties remains strong. In 2023, regulatory changes have prompted many manufacturers to explore sustainable sourcing options, impacting their procurement processes.
- Global Demand: Regions like China and Mexico dominate production, supplying a significant portion of the world's fluorite needs.
- End-User Industries: Key sectors such as aluminum production and other metallurgical operations rely heavily on high-purity calcium fluoride.
"Fluorite's versatility across sectors signifies its essential role in modern industrial processes."
Moreover, pricing trends can also hint at shifting supply chains caused by political or environmental factors. For collectors, understanding what drives current market prices is key to making informed decisions—whether they are looking to add to their collection or resell.
Historical Price Trends
Looking back, historical price trends offer a window into the cyclical nature of the fluorite market. Though prices can vary year by year, patterns often emerge that can predict future movements. For instance, between 2015 and 2019, prices experienced a notable plateau before rising sharply in response to increased industrial capacity in emerging markets.
- Price Fluctuation: Over the past decade, prices have seen a 15% increase on average, with 2020 representing a unique year due to supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic.
- Market Resilience: Post-pandemic recovery has shown a resilient bounce-back, indicating a strong reliance on fluorite in growing economies.
- Collector Impact: Rare colors and specimens generally appreciate more significantly than lower quality varieties. Notable examples, such as the vibrant purple or electric green hues, exhibit this trend—where rarity intertwined with demand can yield exponential value growth.
In summary, the dynamics of the fluote market, combined with historical price trends, create a rich tapestry of information critical for anyone involved in the sphere of fluorite, from eager collectors to savvy investors.
Industrial Applications of Fluorite
Fluorite, known for its vibrant hues and remarkable properties, possesses industrial significance that extends beyond mere aesthetics. The practical uses of this mineral make it a valuable resource across various sectors. Its merits include enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and contributing to product quality. As industries seek to innovate and progress sustainably, fluorite’s roles in manufacturing, energy, and chemical processes are increasingly pertinent. Understanding these applications provides insight into why fluorite remains a sought-after material, illustrating its far-reaching impact on industry and economy.


Uses in Manufacturing and Production
Fluorite finds extensive applications in the manufacturing realm, particularly in the production of aluminum, steel, and optical fibers. Its primary function serves as a flux in metallurgical processes. This means it helps to lower the melting points of materials, facilitating smoother and more efficient production.
- In aluminum production, for instance, fluorite aids in refining bauxite ore. Its presence can significantly improve the extraction processes, making them more environmentally friendly by reducing energy consumption.
- In the steel industry, fluorite assists in removing impurities, ensuring higher-quality steel with fewer defects. The end product, often characterized by strength and durability, is vital for construction and transportation infrastructure.
- Moreover, optical fibers, essential for telecommunications, benefit from fluorite's optic clarity, as it ensures better signal transmission with minimal loss.
In summary, fluorite's multifaceted application in manufacturing underscores its importance and highlights how it contributes to innovation and efficiency.
Role in the Energy Sector
Fluorite’s relevance doesn’t stop at mere manufacturing; it also plays a pivotal role in the energy sector. The substance is critically utilized in the production of hydrofluoric acid, a chemical necessary for various energy-reliant processes. This acid serves as a precursor for several fluorinated compounds, including refrigerants used in cooling and air conditioning systems, which maintain efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.
- Nuclear energy operations also capitalize on fluorite’s properties. It is used to produce uranium hexafluoride, an essential material in the uranium enrichment process for nuclear fuel. Thus, fluorite acts as a linchpin in this complex chain, demonstrating its weighty significance in energy sustainability.
- Additionally, in renewable energy, certain photovoltaic technologies that convert sunlight into electricity utilize fluorite as a component to enhance cell efficiency.
This dependency in energy-related industries marks fluorite as not only a material of choice but also as a component that supports environmental betterment.
Fluorite in Chemical Processes
In the world of chemistry, fluorite’s contribution is nothing short of essential. Its role extends into the creation of chemicals and compounds that drive various industrial applications. One of the most prominent uses is in the manufacturing of hydrofluoric acid—as noted before—which forms the backbone of several chemical processes.
- Fluoropolymers, for example, derived from hydrofluoric acid, are highly valued for their resistance to heat and chemical reactions, making them instrumental in many applications, including coatings and electrical insulations.
- Another noteworthy utilization includes the production of fluorine gas. This gas is vital in producing a range of fluorinated materials, further expanding the applications of fluorite in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other sectors where specialized compounds are necessary.
These chemical processes showcase fluorite’s intrinsic value beyond its surface-level beauty, illustrating a strong intersection between its geological properties and commercial viability.
Fluorite’s contributions to industrial applications not only optimize production processes but also enhance sustainability, marking it as a cornerstone mineral in advancing modern technology.
Ethical Considerations in Fluorite Mining
Mining fluorite, like any resource extraction, comes with a host of ethical considerations that cannot be ignored. As the demand for fluorite continues to grow—driven by its applications in industries such as ceramics, metallurgy, and energy—it's imperative to examine how the extraction of this mineral affects both the environment and the communities involved in mining activities. By addressing the ethical framework surrounding fluorite mining, we bring to light the complexities of resource extraction in today’s world.
Sustainability Practices
Sustainability in fluorite mining centers around methods that not only aim to meet current needs but also ensure that resources remain available for future generations. Companies involved in mining operations are increasingly being held accountable for their environmental footprints. Sustainable practices may involve employing technologies that reduce waste and maximize efficiency during the extraction process. Some operators have turned to more innovative, low-impact techniques that minimize disruption to local ecosystems and wildlife habitats.
Additionally, engaging with local communities to understand their needs and concerns can foster a sense of stewardship over the land. This collaborative approach can lead to better resource management strategies, ensuring that the interests of both the industry and the local populace are respected. Given the critical importance of this resource, laying down guidelines for sustainable practices offers a roadmap for responsible mining that benefits all stakeholders involved.
Environmental Impact Assessments
Conducting thorough Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) is a crucial step in the mining process. These assessments help identify potential adverse effects of fluorite mining on surrounding ecosystems before excavation begins. Factors such as water quality, soil stability, and effects on local wildlife must be rigorously evaluated.
It’s not just about ticking off regulatory boxes; EIAs provide a comprehensive understanding of how mining activities can alter the natural balance. For instance, mining activities could lead to soil erosion, water contamination, and disruption of migratory patterns for local species. Consequently, informed decisions can be made about whether to proceed with a mining operation, modify it for lower impact, or even abandon it entirely if the risks outweigh the benefits.
By raising the bar for environmental scrutiny, the industry can promote greater accountability. This ensures that generations to come inherit a planet that isn't just economically viable but ecologically sound.
"The road to sustainability is paved with commitment and ethics, where every stone counts towards a better future."
Fluorite in the Collectibles Market
Fluorite has made quite a name for itself among collectors, capturing interest not just due to its captivating colors and unique formations, but also because of its diverse applications and rarity. In this segment, we will explore the significance of fluorite in the collectibles market, the reasons for its increasing popularity among enthusiasts, and what collectors should keep in mind when investing in specimens.
Notable Collectible Specimens


Among the most alluring aspects of fluorite for collectors are the distinct varieties that can be found around the globe. Each variation often carries its own story. For instance, the vibrant green fluorite from the Rogerley Mine in England is renowned for its deep color and remarkable clarity. In contrast, the purple fluorite from the Elmwood Mine in Tennessee is often regarded for its striking, rich tones and well-defined crystal formations.
These unique features are not just aesthetically pleasing; they also promote a narrative that appeals to collectors. Moreover, specimens that exhibit interesting crystal formations or contain inclusions like pyrite or quartz can be particularly desirable.
Here is a list of notable fluorite specimens:
- Green Fluorite from the Rogerley Mine: Known for its striking green hue and clarity.
- Purple Fluorite from Elmwood Mine: Valued for its deep purple color and sharp crystal edges.
- Blue Fluorite from the Minerva Mine: Rare and sought after due to its unusual color.
- Color-Zoned Fluorite from China: These possess bands of different colors, making them visually fascinating.
Each specimen tells a story and adds to the intrigue surrounding the collection. As such, passion and knowledge are crucial for collectors.
Value Appreciation of Rare Pieces
When it comes to monetary value, some may think fluorite's allure is merely superficial, but that could not be further from the truth. The value of rare fluorite specimens has seen a remarkable ascent in recent years, driven by both rarity and collector demand. Specimens that once fetched modest prices at local shows have soon seen their worth surge in collectors' circles, especially those with unique characteristics or provenance.
The appreciation in value can be attributed to several factors:
- Rarity: Like anything collectible, rarity significantly influences the price. Specimens that are hard to find often command higher prices.
- Condition: The overall condition of a fluorite piece is essential. Chips, scratches, or cloudy appearances can drastically decrease its value.
- Market Trends: Economic shifts and collector interests can also create fluctuations in the market, making some pieces more valuable than others.
"A rare and pristine fluorite specimen can not only be a source of pride but also a potential investment that appreciates over time."
Fluorite’s dual appeal lies not only in its beauty but also in its ability to serve as a sound investment. As collectors become more discerning and knowledgeable, keeping an eye on market trends, unique pieces can fetch impressive sums, solidifying fluorite's status in the collectible world.
In examining Fluorite in the Collectibles Market, it becomes clear that every rock and crystal has a story to tell and a value that can transcend monetary boundaries. The investment's emotional and historical significance cannot be understated.
Care and Maintenance of Fluorite Collections
Fluorite is a gem that doesn’t just sparkle; it tells a story of nature’s artistry. However, maintaining the beauty and intrinsic value of fluorite collections requires thoughtful attention. Proper care ensures that these vibrant pieces retain their luster and value over time. This section will illuminate the importance of storage and cleaning techniques, providing nuances tailored for collectors who appreciate both the aesthetic and financial aspects of fluorite.
Storing Fluorite Properly
To preserve fluorite’s striking colors and unique crystallographic structures, storage is key. Here are a few critical pointers for keeping these gemstones in tip-top shape:
- Avoid direct sunlight: Fluorite is sensitive to ultraviolet light, which can fade its brilliant colors over time. Store pieces in dark, cool places to minimize exposure.
- Use soft materials: When arranging fluorite crystals, always layer them with soft cloth or felt. This prevents scratches from harder surfaces or other stones, ensuring their surfaces maintain their integrity.
- Group by size and type: While it may be tempting to clump all minerals together, separating pieces into specific types or sizes can prevent accidental chipping from one specimen knocking against the other. If possible, use individual boxes or compartments.
- Temperature awareness: Keep your collection away from temperature extremes, as sudden changes can lead to thermal shock. A stable environment goes a long way in preserving specimen health.
"Proper storage methods significantly reduce the risk of damage, allowing collectors to fully appreciate their investments for years to come."
Cleaning and Preservation Techniques
Regular cleaning ensures that reflections of wonder aren’t dulled by dust and grime. However, caution is necessary. Here’s how to keep your fluorite pristine:
- Gentle washing: For routine cleaning, use lukewarm water and a soft brush to remove dirt. Steer clear of harsh chemicals; they can erode the mineral. Just think of fluorite as delicate as a snowflake on your fingertips.
- Dry with care: After washing, pat the surface dry with a soft cloth. Avoid rubbing, which can contribute to surface scratches.
- Avoid ultrasonic cleaners: These devices can cause damage to fragile minerals. Sticking to manual cleaning techniques keeps your collection safe.
- Display considerations: If showcasing your fluorite, use UV-protective glass for display cases. Besides adding allure to your presentation, this protects against unwanted light exposure.
By adhering to these care and maintenance guidelines, collectors can ensure their fluorite pieces not only radiate beauty but also maintain their financial value for years ahead.
Closure: The Intrinsic and Economic Value of Fluorite
As we wrap up our exploration of fluorite, it’s crucial to reflect on its dual significance—both intrinsic and economic. This mineral is not merely a pretty face in the geological realm; it holds a treasure trove of attributes that make it invaluable to collectors and industries alike.
From a geological standpoint, fluorite’s vibrant colors and its distinct crystal structures signify its potent formation process and adaptability to various environments. Beyond aesthetics, these characteristics increase its allure among collectors and researchers. This mineral showcases a wide array of colors—deep purple, soft green, and vivid yellow—each type hinting at the specific conditions under which it formed. In essence, each crystal tells a unique story.
On the economic front, fluorite serves a purpose that extends well beyond the confines of hobbyist collections. It's heavily utilized in industries such as metallurgy, ceramics, and even the production of fluorine gas. This underscores how deeply intertwined its value is with advancing technological and industrial processes. As the demand for products derived from fluorite continues to grow, its market value is expected to fluctuate, influenced by factors such as availability, quality, and the policies governing mining practices.
Moreover, collectibility is another layer to fluorite’s value. Specimens from unique localities or those exhibiting rare color patterns can skyrocket in price, mirroring broader market trends where rarity drives demand. Collectors often find themselves on the precipice of excitement when they discover a piece that not only embodies aesthetic beauty but also holds significant economic worth.
"Fluorite is a mineral that captivates the eye and the wallet, seamlessly merging beauty with utility."
However, the market is not without its ethical considerations. The balance between mining practices and environmental stewardship plays a vital role in determining whether fluorite can continue to be valued positively or if its extraction will lead to increased scrutiny and backlash from the public and regulatory entities.
In closing, fluorite embodies a fascinating intersection of beauty and functionality. Its intrinsic value lies in its unique properties and the geological processes that create it, while its economic value is reflected in its versatility and demand across various sectors. For collectors, understanding both aspects can enhance appreciation and inform better investment practices. As the world evolves, so too will the value of fluorite, making it a mineral worth watching.