Discovering the Intricacies of Hemimorphite Mineral
Intro
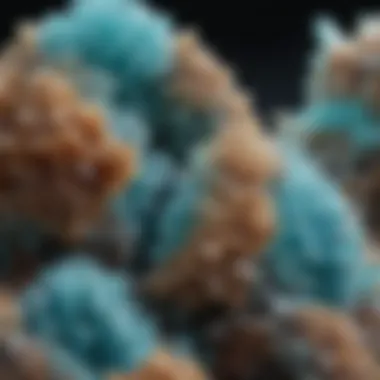
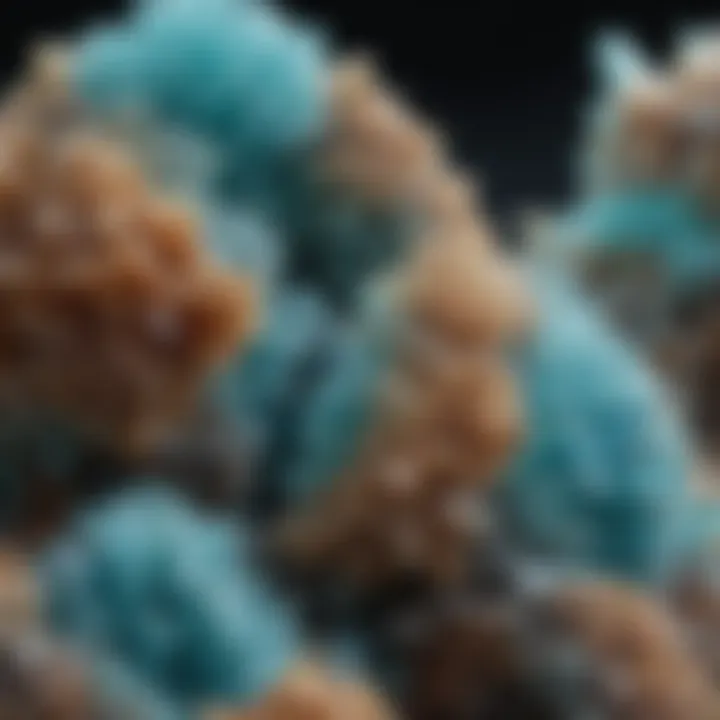
Hemimorphite is not just any old mineral; it’s a fascinating gem that captures the attention of collectors and geologists alike. Found in various geological formations, hemimorphite is unique in its crystalline structure, showcasing what can only be described as a mesmerizing blend of beauty and intrigue. As we dive deeper into its wilderness, this article seeks to illuminate the many dimensions of hemimorphite – from how it forms deep within the Earth to why it's become a sought-after collectible among enthusiasts.
Overview of the Topic
Definition of Key Terms
To appreciate hemimorphite fully, it’s vital to establish some foundational definitions. Hemimorphite is a zinc silicate mineral chemically composed of zinc silicate hydroxide, often presenting as colorless, white, or sometimes blue crystals. The term "hemimorphite" derives from the Greek words "hemi," meaning half, and "morphe," meaning form, reflecting its unique crystallography where one end of the crystal might differ from the other.
Historical Significance
Historically, hemimorphite has seen a robust journey through both science and society. It was first identified in the early 19th century and has since been a part of various mineral collections around the world. Its aesthetic appeal draws many to purchase it for decorative purposes, while its rarity makes it a trophy find for serious collectors. Moreover, hemimorphite has been used in jewelry, traditionally believed to offer protective properties to the wearer, which adds another layer of significance.
Types of Collectibles
Classification of Different Collectibles
When one thinks of mineral collectibles, the world can be seen as a vibrant tapestry woven with various threads. Hemimorphite fits into the larger realm of mineralogy, where collectors categorize specimens based on criteria such as color, size, shape, and locality. Categories can be divided into:
- Aesthetic Collectibles: Those appreciated for their beauty, like well-formed crystals.
- Scientific Samples: Specimens used for educational purposes or research.
- Historical Pieces: Minerals linked to specific events or discoveries.
Notable Categories
Some specific categories that hemimorphite can fall into include:
- Blue Hemimorphite: Known for its striking azure hues, it captivates many collectors.
- Botryoidal Hemimorphite: The rounded, grape-like formation of this variety is visually appealing and often sought after.
- Crystal Clusters: Specimens presenting multiple crystals growing together form an attractive addition to any collection.
"A mineral isn’t just a rock; it often carries stories of its own - tales of earth’s dynamic processes and the human hands that cherish them."
As we continue through this exploration of hemimorphite, the intricacies of its processes and uses will unravel. Each nugget of information aims to not only enrich the minds of collectors but also deepen the appreciation for this striking mineral.
Foreword to Hemimorphite
Hemimorphite is a mineral that captures the interest of both scientists and collectors alike. Its intricate crystalline structure, showcasing unique forms, makes it an object of fascination. Moreover, this mineral serves more than just aesthetic purposes; it holds significant value in various applications, from industrial use to gemstone collection. Understanding hemimorphite's importance is crucial to appreciating its multifaceted roles in geology, mineralogy, and economic sectors. In this section, we will explore the mineral further and delve into its historical context that shapes our understanding today.
Understanding the Mineral
Hemimorphite, chemically formed as zinc silicate, is typically found in the form of delicate crystals that can appear quite striking in their beauty. These crystals can range from colorless to vibrant blues and greens, often resembling aquamarine or turquoise. The term "hemimorphite" itself reflects its unique crystalline properties, as it derives from Greek meaning "half form". Notably, what makes hemimorphite distinct is its hemimorphism, meaning that while one end of the crystal is composed of different atoms than the other, this phenomenon is not common in most minerals.
From an aesthetic standpoint, hemimorphite is often sought after by collectors. The mineral tends to form in a variety of interesting shapes, including massive and botryoidal (grape-like) formations, making it a wonderful addition to any gem collection. The clarity of certain specimens can enhance their allure, making high-quality hemimorphite quite valuable.
Historical Context
The history of hemimorphite spans several centuries and intertwines with the broader narrative of mineralogy's evolution. Initially, hemimorphite was misclassified, often confused with smithsonite, another zinc carbonate mineral. It was in the early 19th century that more distinct characteristics were recognized. This period marked a pivotal shift in scientific inquiry, as the mineral was identified and classified properly in a time when minerals were not just scientific curiosities but also held economic value.
Throughout history, hemimorphite has held cultural significance, particularly in Europe and the Americas, where it was associated with various uses, from a source of zinc to a decorative stone in jewelry. The booming mining industry during the 19th century significantly impacted the prominence of hemimorphite, as miners sought to extract not just metals but also the beautiful specimens for collectors. This intertwining of economic factors and aesthetic appeal laid the foundation for hemimorphite as a cherished collectible, setting the stage for its enduring popularity today.
As we continue exploring hemimorphite, it becomes evident that understanding both its physical traits and historical journey adds layers to our appreciation of this remarkable mineral.
Geological Formation of Hemimorphite
Understanding the geological formation of hemimorphite is essential for anyone keen on delving into its attributes and origins. Hemimorphite stands out not just for its aesthetic allure, but also for the intriguing processes that contribute to its creation. This section aims to shed light on how this mineral forms, focusing on the unique geological conditions and relationships it holds with other minerals.
Geological Processes
The formation of hemimorphite is a remarkable process influenced by a variety of geological factors. This mineral often originates from the hydrothermal alteration of zinc-rich deposits. In simpler terms, hemimorphite is born when hot, mineral-laden water seeps through rock formations, which contain zinc and other elements. Over time, as this heated water moves and cools, the conditions create the perfect environment for hemimorphite crystals to develop. The key here is temperature and pressure, both of which play critical roles in stabilizing the structures of these crystals.
Moreover, hemimorphite can also form through other processes, such as weathering. Think about it: factors like wind and rain can wear down primary minerals, leading to the leaching of zinc, which then crystallizes as hemimorphite. This transformation reflects nature’s methodical approach, crafting minerals out of raw elements. This versatility in formation helps scientists understand environmental conditions and historical geological events.
Locations and Environments
The locations where hemimorphite is found are as varied as its formation processes. It typically occurs in sedimentary rocks and can also be discovered in regions rich in zinc and lead. What makes these sites interesting is not just the mineral itself but the geological history they tell.
Notable Deposits
Among the most noted deposits of hemimorphite can be found in places like the Tsumeb Mine in Namibia and the famous Dal'negorsk in Russia. These locations not only provide hemimorphite of exceptional quality but also showcase stunning crystal formations that pique the interest of many collectors. The Tsumeb Mine is renowned for its vibrant color range and impressive size of specimens, making it a haven for collectors who appreciate aesthetic quality. The unique geological complexities of these sites allow hemimorphite to grow in surreal forms, sometimes resembling flowers or other intricate shapes. The characteristics of hemimorphite here underscore why such deposits are highlighted in discussions about the mineral—as they provide collectors with both beauty and value.
Moreover, these deposits often yield rare specimens that can skyrocket in value, especially when paired with flawless crystalline structures.
Global Distribution
When discussing the global distribution of hemimorphite, it’s intriguing to note how widespread this mineral is. It has been found in multiple countries around the world, from Mexico to Greece, indicating its adaptability to different environmental conditions. Each region contributes distinct characteristics to the mineral. For instance, hemimorphite from Mexico typically displays different colors and patterns when compared to specimens from Europe.


This wide distribution is beneficial for collectors, as it opens up avenues for sourcing various forms and styles of hemimorphite. However, it can also lead to confusion, as similar-looking minerals exist. Understanding the geographic origins can help distinguish hemimorphite from other minerals like smithsonite or certain calcites, which sometimes masquerade under similar appearances.
The unique features of global specimens can add depth to a collector's understanding and appreciation; collecting specimens from different regions can serve as a gallery of the mineral's extensive attributes.
"The geological journey of hemimorphite from underground formations to collector's shelves illustrates the beauty found in natural processes."
Collectively, the geological formation, locations, and environmental factors contribute to the sophisticated narrative of hemimorphite. This mineral not only sparks curiosity but also captivates rock collectors and enthusiasts, offering layers of intrigue that go far beyond captivating appearances.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Understanding hemimorphite’s physical and chemical properties is essential when diving into the world of mineralogy and collecting. This segment highlights how these properties can influence not only the mineral's aesthetic appeal but also its applications in various fields. Hemimorphite's characteristics serve both enthusiasts and industry professionals alike, making this section crucial to grasp.
Crystalline Structure
The crystalline structure of hemimorphite is quite distinctive, classified under the Zinc Silicate group. It's known for its hemimorphic structure, which essentially means that its two ends display different crystalline forms. One end is typically smooth, while the other might be more irregular or rugged. This unique formation can help collectors identify genuine specimens.
Crystallization occurs mostly in the trigonal system, leading to prismatic or acicular (needle-like) crystals. The hexagonal symmetry of the crystals makes them particularly striking, especially when light refracts through them. Beyond aesthetic value, this structure also indicates how the mineral forms under specific environmental conditions, adding an element of geological significance.
Chemical Composition
Delving deeper into hemimorphite’s chemical makeup, it primarily consists of zinc, silicon, and oxygen. Its chemical formula can be denoted as Zn4Si2O7(OH)2·O, showcasing the hydroxide and water content, which highlight the mineral's hydration state. The presence of zinc plays a significant role in its use as a raw material in the metal industry, especially for the production of brass and other alloys.
The combination of elements is also why hemimorphite is frequently confused with other minerals, particularly smithsonite. However, the ratios and specific arrangements of the atoms are what set each mineral apart. Understanding this composition is particularly useful for collectors and researchers seeking to study the formation processes of minerals in varying environments.
Optical Characteristics
One of hemimorphite's most amazing features is its optical properties. When it comes to visual appeal, nothing quite compares to its potential for color and clarity. Specimens can display soft shades of blue, green, and yellow, while also exhibiting a transparency that catches the eye. These color variations can be attributed to trace impurities during crystallization, causing shifts in appearance under different lighting conditions.
The mineral also possesses birefringence characteristics, which means the way it interacts with light can change depending on the direction of that light. This property is particularly intriguing for gem enthusiasts and can be witnessed when placing a piece under polarized light. It adds layers of depth to the stone, enhancing its allure for collectors.
"The beauty of hemimorphite is not just skin deep; it reflects the intricate processes that shaped its existence over millennia."
These optical characteristics make hemimorphite not just a favorite among collectors but also a subject of interest in scientific studies regarding mineral optics and crystallography. Collectors who appreciate the allure of these specimens often use them to draw connections between geological history and contemporary mineral collecting practices.
Understanding these physical and chemical properties of hemimorphite allows enthusiasts to appreciate the mineral on a deeper level, recognizing not just its beauty but also the complex systems that govern its formation and identity.
Uses and Applications
Hemimorphite offers various applications across different sectors, showcasing its versatile character. This section aims to shed light on the significance of hemimorphite in both industrial contexts and its desirability in the gemstone market. Understanding these uses not only enhances the appreciation of this mineral but also positions hemimorphite as a key player in numerous fields.
Industrial Applications
Use in Ceramics
In the realm of ceramics, hemimorphite stands out for its prominent role in crafting vibrant glazes and pottery. The mineral's properties contribute to the smooth finish and unique textures that many artisans aspire to achieve. Its availability in fine powder form allows for an even mixture with other materials, enhancing the aesthetic qualities of the final product.
Key Characteristic: Hemimorphite provides color variance, which is a highly sought-after trait in artistic ceramics. Its natural hues can lend depth and richness to ceramic pieces.
However, there is a flipside; the incorporation of hemimorphite can also present challenges, particularly its weight. While beneficial for specific applications, heavier products can create logistical issues in shipping and handling.
Role in the Chemical Industry
Hemimorphite finds an essential place in the chemical industry, particularly in zinc extraction processes. For years, it has been recognized for its capability to serve as a source of zinc, a vital element in numerous chemical applications including batteries and corrosion-resistant coatings.
Key Characteristic: The distinctive chemical structure of hemimorphite allows it to be utilized efficiently for extracting pure zinc. This is particularly advantageous because it can lead to reduced environmental impact compared to other extraction methods.
Nonetheless, the dependency on hemimorphite can fluctuate with market availability. When supply chains are disrupted, industries may face delays, hindering production schedules.
Gemstone and Collectible Value
Market Trends
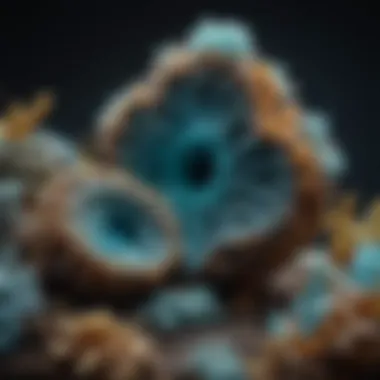
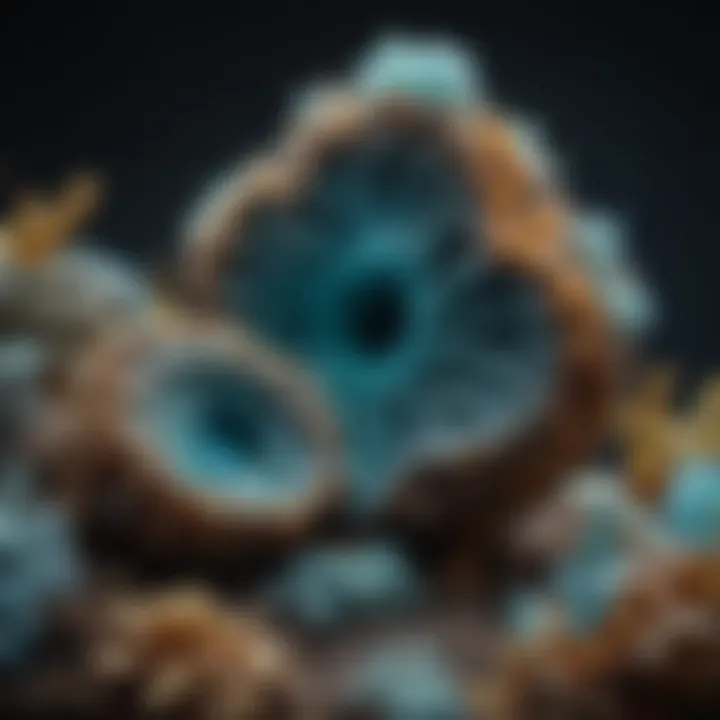
The market for hemimorphite as a gemstone has seen an uptick, revealing an increasing interest from collectors and enthusiasts. This mineral's unique crystalline structure and color variations make it a compelling addition to any collection. Its aesthetic appeal can drive prices higher as demand grows.
Key Characteristic: Its visual properties and rarity have positioned hemimorphite as an attractive investment for collectors. Trends indicate that rarer specimens, particularly those with unique inclusions, fetch higher prices.
A challenge to keep an eye on is the potential for overexploitation. As more people appreciate hemimorphite, the pressure on sources could rise, which may impact availability and prices in the long run.
Factors Affecting Demand
The demand for hemimorphite is influenced by several factors, including market accessibility, specimen quality, and the overall health of the gemstone market. As interest in mineral collecting increases, newer collectors may drive the demand, pushing prices upward.
Key Characteristic: The mineral's status in pop culture and media also affects market demand. Appearances in crystal healing circles have garnered a renewed interest in its properties, further solidifying its place in the market.
However, it is prudent for both new and seasoned collectors to be cautious of artificial inflation of prices. Assessing the authenticity and quality of pieces is crucial to ensure a sound investment.
"In the world of minerals, the butterfly effect is real; changes in one market can create ripples through others."
The interconnected nature of hemimorphite’s applications and its status as a collectible illustrates its multifaceted value. Understanding these dynamics not only enriches the knowledge surrounding hemimorphite but also equips collectors and industry players with insights into future trends.
Collecting Hemimorphite
Collecting hemimorphite can be a deeply rewarding endeavor, appealing to those who appreciate its unique properties as well as those looking to enhance their mineral collections. One of the most fascinating aspects of this mineral lies in its distinctive crystalline structure and the array of colors it presents. Whether you're a seasoned collector or just dipping your toes into the world of minerals, understanding how to collect hemimorphite can bring joy and insight into this specialized hobby.
How to Identify Quality Specimens
When it comes to identifying quality hemimorphite specimens, there are several key features to examine. First off, look for clarity and brilliance; high-quality pieces have a translucent appearance that allows light to pass through, highlighting their unique colors and patterns. Setting your eyes on the crystal formation is equally vital—the best samples exhibit well-defined and distinct crystalline shapes.
In addition, evaluate the color. Hemimorphite can appear in a spectrum that includes blues, greens, and whites. Specimens with rich, vibrant colors often catch the eyes of collectors and can be quite valuable. Lastly, check for any visible damage or imperfections; chips and breaks can diminish a specimen’s value significantly. In summary, quality specimens are typically characterized by:
- Clarity and transparency
- Well-defined crystalline structure
- Vibrant colors
- Lack of damage
Tips for Beginner Collectors
For those who are just starting out in the mineral collecting scene, it can seem overwhelming. Here are a few tips to get your journey moving in the right direction:
- Research: Before making any purchases, take the time to learn about hemimorphite, its properties, and the differences among various specimens.
- Buy from Reputable Sources: Always purchase from trusted dealers or reputable shows where authenticity is guaranteed.
- Network: Engage with other collectors—even a casual conversation may introduce you to valuable insights and opportunities.
- Start Small: Begin with smaller specimens to build your knowledge and confidence before committing to larger, more expensive pieces.
- Keep Records: Document your collections with detailed notes including where you acquired each piece, its price, and any unique characteristics.
Connecting with the Community
Building connections within the collecting community can be immensely beneficial for both learning and sharing your passion. Two noteworthy avenues to explore are local clubs and online platforms.
Local Clubs and Societies
Local clubs and societies provide an excellent opportunity to interact with like-minded individuals. These organizations foster a sense of camaraderie among collectors while offering activities such as field trips, guest speakers, and educational workshops. Engaging with these clubs can be a beneficial choice for any collector, especially beginners who appreciate hands-on advice and mentorship. The unique aspect of these societies is that they often bring together diverse knowledge; even a short chat can offer insights on rare finds or ethical collecting practices.
- Advantages: Direct interaction with experienced collectors, hands-on workshops, and local field trips.
- Disadvantages: May require a time commitment and membership fees, which could discourage some individuals.
Online Platforms
In our digital age, online platforms offer a different flavor of connectivity, enabling collectors to share resources, discuss findings, and even trade or purchase specimens. Websites like Facebook and Reddit host numerous groups focused on mineral collecting, where members exchange knowledge and support.
One of the key benefits of online platforms is accessibility. Whether it’s a Facebook group or a dedicated forum on Reddit, potential collectors can access a wealth of information and opinions at their fingertips. The downside, however, is the potential for misinformation. So, as you dive into these discussions, it’s crucial to approach with a critical eye and verify information through reliable sources.
- Advantages: Accessibility to information and a broad audience for networking.
- Disadvantages: Risks of misinformation and lack of personal interaction.
"Collecting minerals like hemimorphite isn't just a hobby; it's about forming connections with nature and with fellow enthusiasts."
Cultural and Symbolic Significance
The cultural and symbolic significance of hemimorphite stretches far beyond its physical properties. For many societies, it embodies more than just a mineral; it represents beliefs, stories, and values that resonate with individuals on various levels. This significance enhances the appreciation for hemimorphite, making it more than a mere collectible. Its influence can be traced throughout history, reflecting human emotion and dedication to the natural world.
Historical Beliefs
In ancient cultures, crystals were often seen as vessels of spiritual energy. Hemimorphite, due to its striking appearance and unique formation, was no exception. Many civilizations, particularly in regions where this mineral was found, believed hemimorphite held protective properties. They considered it a shield against negativity, attributing to it the power to promote healing and emotional stability.
In the lore of certain Native American tribes, for instance, this mineral was believed to draw strength from the Earth. An old tale tells of a medicine man who used hemimorphite in rituals to connect with the spirits of the ancestors, reflecting a deep respect for the land and its natural components.
Artifacts adorned with hemimorphite have been discovered in archaeological digs, suggesting that it held significant value and was possibly used in talismans or ceremonial items. Such historical practices show how deeply intertwined hemimorphite was with cultural identity, shaping beliefs and practices in ways that remain influential.
Modern Interpretations
Fast-forward to the present, and hemimorphite continues to inspire both art and personal expression. In modern metaphysical circles, it is often linked with clarity of thought and creativity. Collectors value it not just for its beauty but also for its purported abilities to promote inner peace and clarity. Many enthusiasts believe that wearing hemimorphite can enhance communication, encouraging individuals to express their thoughts and feelings more freely.
Social media platforms, particularly Facebook and Reddit, have become hubs for discussions about the metaphysical properties of hemimorphite. Here, community members exchange personal anecdotes about how the mineral has influenced their lives, often focusing on overcoming challenges or enhancing emotional well-being. This modern narrative adds layers of meaning, transforming hemimorphite from a natural resource into an integral part of many personal journeys.
Importantly, while many embrace the symbolic aspects of hemimorphite, others approach it purely from a geological or collectible standpoint. This creates a rich tapestry where science and spirituality coexist, prompting an ongoing dialogue about the role of such minerals in our lives.
"The significance of hemimorphite lies not just within its crystalline beauty, but in the stories it embodies across cultures and time."
With both historical and modern contexts considered, hemimorphite emerges as a mineral of profound significance—inspiring respect, fascination, and connection among those who encounter it.
Comparison with Similar Minerals
Understanding the differences and similarities between hemimorphite and similar minerals can guide collectors in distinguishing these unique specimens. This section not only emphasizes the distinct characteristics of hemimorphite but also highlights the interconnectedness of this mineral within its broader geological family. Collecting becomes more than just an exercise in aesthetic appreciation; it develops into an informed journey that unravels the complexities of mineral identification and valuation.
Differences from Smithsonite
At first glance, hemimorphite and smithsonite can be mistaken for each other due to their similar appearances. However, understanding their differences is crucial for collectors who wish to add unique specimens to their collection.
- Chemical Composition: One of the key distinctions lies in their chemical makeup. Hemimorphite has the chemical formula Zn4Si2O7(OH)2·O, whereas smithsonite, a much sought-after mineral, has the formula ZnCO3. This difference in composition not only affects their physical properties but also their crystalline structure and formation.
- Crystalline Structure: Hemimorphite often exhibits a distinctively hemimorphic crystalline structure. It tends to grow in elongated, prismatic crystals that can be clear to cloudy in appearance. In contrast, smithsonite tends to manifest in more rounded, botryoidal forms, resembling little beads or grapes. These differences can significantly affect their appeal to collectors.
- Color Variance: While both minerals may display shades of blue, green, or yellow, smithsonite often presents more vivid coloration, especially in the presence of impurities. Hemimorphite’s colors tend to be softer and more pastel-like, showcasing delicate shades.
- Locality Factors: Their geographic distribution also sets them apart. Hemimorphite often forms in the oxidized zones of zinc deposits, like those found in the famous mines of Tsumeb, Namibia, while smithsonite can be found in copper-rich environments, which leads to different mining locations and, potentially, different collecting opportunities.
Understanding these distinctions helps collectors value each mineral on its own terms while also enhancing their appreciation for the broader category of zinc-bearing minerals.
Similarities with Zinc Minerals
Hemimorphite shares notable similarities with other zinc-related minerals, enhancing its allure for rock and mineral collectors. These similarities often revolve around the mineral’s composition and the geological processes that lead to their formation.
- Chemical Family: Both hemimorphite and many other zinc minerals, such as sphalerite, share zinc as a central component. This familial relationship often leads to similarities in their formation conditions and metallic luster.
- Formation Process: Hemimorphite and these other minerals typically form under similar geochemical conditions, especially in environments where oxidation processes prevail. This can lead to overlaps in their accretion scenarios, making the study of their formation insightful for both geologists and collectors.
- Appeal to Collectors: Just as with hemimorphite, other zinc minerals often boast stunning colors, lustrous surfaces, and unique crystal habits. These attributes make them highly sought after in the collector’s community. As collectors expand their collections, these similarities offer opportunities to explore the interconnected world of zinc minerals further.
It's crucial for enthusiasts to have a well-rounded understanding of these aspects. This opens avenues to delve deeper into mineral characteristics and their geologic history, enriching both the collecting experience and scientific appreciation.
Environmental Considerations
The environmental implications of mineral extraction play a pivotal role in any discussion about hemimorphite. Given its distinctiveness and popularity, understanding these factors is not merely academic; it’s essential for future generations of collectors and researchers. Mining activities, while necessary for gathering this stunning mineral, can have far-reaching effects on ecosystems. From habitat destruction to pollution, the ramifications of sourcing hemimorphite cannot be overlooked.
Impact of Mining
Mining for hemimorphite and other minerals often disturbs local environments. Take the example of some regions in Mexico, which are known for their rich hemimorphite deposits. The extraction process can lead to soil degradation, disrupting local flora and fauna. The disturbances can also affect water quality, particularly if harmful chemicals are utilized in the mining process.
Moreover, operational mining sites may create waste that, if not managed properly, can find its way into nearby waterways, affecting fish populations and the broader ecosystem. The potential loss of biodiversity, alongside impacts on local communities that rely on these natural resources, presents a significant challenge.
Notably, mining companies are increasingly scrutinized, and regulatory frameworks are evolving to minimize these negative impacts. It’s crucial for collectors and enthusiasts to understand that the beauty of hemimorphite comes at a cost, and being mindful of these environmental impacts can foster a more sustainable approach to mineral collection.
Sustainability Practices
As awareness of environmental issues grows, sustainable practices in mining have become not just an option but a necessity. Some companies are now implementing strategies that prioritize minimal environmental disruption. Efforts like using less invasive mining techniques and investing in land reclamation initiatives can help mitigate the damaging effects of extraction.
Furthermore, sustainable practices extend beyond the site of extraction. It involves engaging with local communities to ensure that mining benefits all parties involved.
Here are several sustainable practices related to hemimorphite mining:
- Eco-Friendly Extraction Methods: Utilizing technology that reduces the impact on the surrounding habitat, such as selective mining methods that leave less waste.
- Reclamation Projects: Actively restoring mined land to its original condition after extraction, aiming to revive ecosystems and habitats.
- Water Management: Implementing systems to treat wastewater and prevent contamination before it reaches natural water bodies.
- Community Engagement: Collaborating with local stakeholders for responsible mining practices that consider community needs and environmental health.
Taking these steps not only protects the planet but also enhances the reputation of the mineral collection community as a whole. Collectors can play a vital role in promoting sustainable practices.
To truly appreciate hemimorphite's beauty, we must also respect the land it comes from.
Research and Scientific Studies
Research and scientific studies are crucial to comprehensively understanding hemimorphite. This mineral, with its distinctive properties and varied applications, continues to intrigue scientists, geologists, and collectors alike. The examination of hemimorphite is not merely an academic pursuit; it significantly contributes to advancements across various fields, from material science to environmental sustainability.
By studying hemimorphite, researchers can uncover insights into its formation, structure, and the underlying processes that influence not just this mineral but also similar zinc-bearing minerals. These studies aid in innovative industrial applications, attracting attention for both scientific inquiry and practical uses.
Recent Findings
Recent studies have expanded our knowledge of hemimorphite in several ways. For instance, one notable research discovery involved the identification of trace elements within hemimorphite that were previously undocumented. This has implications for collectors, enhancing the value and appeal of certain specimens.
Studies have also examined how hemimorphite can be utilized in cleaning up toxic waste. With its unique composition, this mineral shows potential in adsorbing heavy metals from contaminated sites, which is an exciting development in environmental science. Furthermore, the properties of hemimorphite are being explored for potential use in the development of innovative ceramics and other materials.
"The intersection of mineralogy and environmental sustainability is where the future of research lies. Hemimorphite is leading the way in this exploration."
Future Research Directions
Looking ahead, several intriguing avenues for future studies on hemimorphite are emerging. First, the quest to understand its crystallization processes could yield valuable insights that might be useful in synthesizing similar minerals in laboratory settings.
Another potential area of exploration is the technological applications of hemimorphite. Researchers can investigate its use in energy-efficient processes or in the production of sustainable materials. Additionally, interdisciplinary collaborations that bring together mineralogists, material scientists, and environmental engineers could open doors for groundbreaking innovations.
Finally, as interest in rock collecting grows, studies focusing on hemimorphite’s aesthetic and commercial appeal could provide vital data to better serve the collector community. Understanding what drives demand, alongside the unique characteristics of different specimens, may help collectors make more informed choices and enhance their collections.
Culmination
In contemplating hemimorphite, one might conclude this mineral embodies far more than mere aesthetics; it encompasses a spectrum of geological, historical, and practical dimensions. Each facet explored in this article not only deepens our understanding of the mineral itself but also elevates its significance among rock and fossil enthusiasts.
Summary of Key Points
To bring clarity, the key highlights of our exploration include:
- Geological Formation: Hemimorphite results from specific geological processes, predominantly the oxidation of zinc-bearing minerals. Locations, such as the famous deposits in Mexico and Germany, have been pivotal in revealing its rich formations.
- Physical and Chemical Properties: With a unique crystalline structure and striking visual characteristics, hemimorphite intrigues both scientists and collectors alike. Its chemical composition varies among deposits, showcasing a range of hues from blue to green.
- Uses and Applications: Beyond its beauty, hemimorphite finds industrial applications particularly in ceramics and the chemical sector. The distinct visual appeal also renders it a sought-after gemstone, enhancing its market value.
- Cultural Significance: The mineral's historical context stems from various cultures believing in its healing properties and value in craftsmanship. Modern interpretations continue to acknowledge this cultural heritage.
- Environmental Considerations: The impact of mining practices highlights the importance of sustainability, shedding light on modern efforts to mitigate ecological consequences while still allowing collectors to enjoy this fascinating mineral.
Final Thoughts on Hemimorphite
In sum, hemimorphite emerges not just as a collector's prize but as a subject of scientific merit worthy of continued study. The interplay of its geological history, utility, and cultural significance paints a portrait of a mineral that resonates across various spheres.
By integrating these various threads into our understanding, enthusiasts can appreciate hemimorphite not just as a beautiful specimen but as a narrative—of Earth’s processes, human creativity, and the ongoing dialogue between nature and culture.
"Understanding a mineral like hemimorphite allows us to grasp the deeper connections between the Earth and our human experience."
The journey of exploring hemimorphite, from its formation to its current status among collectors, illuminates its complex nature and enhances our appreciation for the world beneath our feet.















