Exploring the World of Fluorescent Rocks
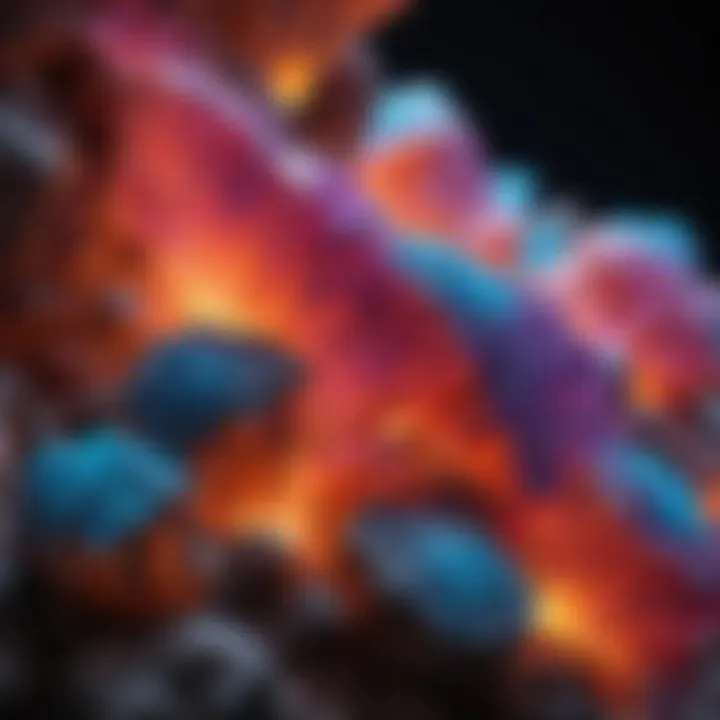


Intro
Fluorescent rocks are a captivating niche within the realm of geology, showcasing a dazzling range of colors and light displays when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. This characteristic luminescence not only enchants rock and mineral collectors but also opens avenues for scientific inquiry. The allure of these minerals often prompts folks to delve deeper into their well of knowledge, uncovering the interplay between nature and light.
These vibrant specimens, often found in a variety of geological settings, possess a unique charm that attracts both seasoned collectors and curious novices. Understanding what makes these rocks glow can enhance appreciation and inform proper collection methods, making the journey into the world of fluorescent minerals both informative and exciting.
Thus, this comprehensive guide seeks to illuminate the essential aspects of fluorescent rocks, from their early historical significance to practical considerations for collectors today.
Prolusion to Fluorescent Rocks
The study of fluorescent rocks is more than just a niche interest for geology enthusiasts; it opens the door to understanding the intricate processes behind their captivating glow. For rock and fossil collectors, these luminescent specimens are not merely beautiful to behold but also offer a wealth of scientific knowledge. By delving into fluorescent rocks, one can uncover a trove of insights into mineral composition and the environmental conditions that led to their formation.
Definition and Characteristics
Fluorescent rocks are those that emit visible light when exposed to ultraviolet light. This luminescence occurs when minerals absorb the UV rays and then re-emit them at a longer wavelength. Characteristics of fluorescent minerals can vary widely, with some displaying vibrant colors like greens, yellows, and pinks, while others may emit a soft, subdued glow. For example, fluorite is widely known for its striking fluorescence, commonly showing blue or green hues, depending on impurities present within the crystals.
The mechanisms of fluorescence can be influenced by many factors, including the rock's chemical makeup and the type of impurities or activators that are present. Notably, minerals such as calcite and willemite also present remarkable fluorescence but differ in their activation energy levels, leading to distinct visual effects. Understanding these attributes is crucial for any collector who wishes to appreciate and identify these rocks effectively.
Historical Overview
The fascination with fluorescent rocks isn't a modern phenomenon; it's been a topic of intrigue for centuries. The first well-documented instance of fluorescent minerals dates back to the late 19th century when researchers began exploring the properties of minerals under various light sources. Notably, George Stokes, a British scientist, was instrumental in defining the term "fluorescence" during his research on minerals. His findings paved the way for future studies in the field.
Over the years, the allure of fluorescent rocks has captivated collectors, scientists, and even artists, leading to a surge in popularity. As more individuals developed an interest in the geological phenomena, museums began to exhibit fluorescent specimens, showcasing the beauty and complexity of these natural wonders. Events like rock shows and mineral fairs have also emphasized their importance, serving as gathering grounds for enthusiasts to trade and display stunning fluorescent minerals.
The Science Behind Fluorescence
The exploration of fluorescent rocks isn't just a whimsical journey into a world filled with colorful glowing minerals; it's deeply rooted in scientific principles. Understanding the science behind fluorescence reveals not only how these minerals emit light but also highlights the transformative beauty present in nature's creations. This section lays down the foundational concepts surrounding luminescence, chemical composition, and light's role in activating these mesmerizing displays.
Understanding Luminescence
Luminescence is a broad term referring to the emission of light by a substance not resulting from heat. This phenomenon occurs in various forms, including fluorescence, which is specific to the absorption and re-emission of light. When we talk about fluorescent minerals, we refer to those that can absorb ultraviolet light and subsequently emit visible light, creating stunning visual effects.
The process of fluorescence is quick; a mineral might glow vibrantly under UV light, but the glow disappears almost immediately once the source of light is removed. This characteristic differentiates fluorescence from phosphorescence, where the glow lingers on for some time after the light source is removed.
"The fascinating brilliance of fluorescent rocks reveals nature's hidden artworks, showcasing how minerals interact with light."
Chemical Composition and Fluorescent Minerals
One of the key elements contributing to a mineral's fluorescence is its chemical makeup. Specifically, certain metal ions present in the crystalline structure can absorb ultraviolet light. For instance, minerals like calcite and fluorite owe their characteristics to the presence of trace elements such as manganese or uranium within their composition. Understanding these components is crucial for collectors since it gives insight into what makes a specific mineral fluorescent or not.
Here are a few common fluorescent minerals and their noteworthy components:
- Fluorite: Exhibits various colors depending on the presence of impurities such as yttrium and cerium.
- Willemite: A zinc silicate that shows bright green fluorescence, often caused by the excitation of zinc.
- Sodalite: Typically glows under UV light due to sodium's unique interactions within its structure.
Recognizing the chemical aspects of minerals allows rock and fossil enthusiasts to better appreciate their collections, knowing they are not just observing pretty stones but small treasures shaped by science.
Role of Natural and Artificial Light
Light is the catalyst that brings fluorescent minerals to life, and understanding its role helps collectors plan better display methods and collecting strategies. There are two main categories of light that can reveal fluorescence: natural light (like ultraviolet light found in sunlight) and artificial light (usually sourced from specialized lamps).
Natural light, particularly when filtered by the atmosphere, has a specific intensity and wavelength that might not be reliably replicable in all locations. This fact presents both opportunities and challenges for collectors looking to observe fluorescence in the wild. Outdoor expeditions during certain times of the day, especially on sunny afternoons with clear blue skies, may yield surprisingly vibrant colors in minerals.
On the other hand, artificial light sources like longwave and shortwave UV lamps are critical for indoor displays and research purposes. When using these, it’s important to be cautious. The intense rays can be harmful, so ensuring proper shielding or protective eyewear is not only a good practice but is paramount to safety. Collectors should take note of:
- Wavelength: Using the right type of UV light for effective fluorescing.
- Duration: Prolonged exposure can sometimes alter the appearance or damage the minerals.
By becoming familiar with how various light sources interact with fluorescent minerals, collectors can elevate both the enjoyment and preservation of their prized collections.
Types of Fluorescent Rocks


Understanding the various types of fluorescent rocks is crucial for both collectors and enthusiasts. This knowledge helps to guide exploration efforts and fosters deeper appreciation of these gems from the earth. Fluorescent minerals display unique visual elements that can be captivating to anyone with an eye for detail. Recognizing these minerals not only broadens one’s collection but also adds value to it.
Examples of Common Fluorescent Minerals
When delving into the world of fluorescent rocks, several minerals commonly catch the collector’s eye due to their remarkable luminescence. Some of these include:
- Fluorite: One of the most recognized fluorescent minerals. It exhibits a stunning range of colors, which can appear vibrant under ultraviolet light. Collectors are often drawn to its both cubic formations and hue variety.
- Calcite: Especially when colored, calcite can show bright fluorescence. The mineral also has the ability to fluoresce in different colors depending on the impurities present.
- Willemite: Known for its bright green fluorescence, willemite can make an impressive addition to any collection. It often occurs in zinc deposits, providing both beauty and a geological story.
- Scheelite: Notable for its blue-white glow under UV light, scheelite is another mineral enthusiasts seek. It often forms in veins, often associated with tin deposits.
The allure of these minerals is not only their colors but their formation processes, often deeply intertwined with the earth's geological history.
Rarity and Value
Rarity is one of the many factors that elevate the desirability and, consequently, the value of fluorescent rocks. Certain minerals can be quite scarce, while others are more abundant. Here are some aspects to consider:
- Scarcity: Minerals such as crawfordite—which shines with coppery hues under UV light—are significantly less abundant than common types like calcite or fluorite. This rarity often translates to higher prices in the collector’s market.
- Quality of Fluorescence: The intensity and clarity of a mineral's fluorescence can drastically impact its value. Minerals that display bright and consistent luminescence fetch a higher price.
- Geological Context: A mineral’s place of origin can add historical value to it. For instance, minerals sourced from renowned localities often hold extra weight in terms of collectible desirability.
- Condition: Well-preserved specimens, free from damage or weathering, are more sought after. This means both novice and experienced collectors should focus on proper care and storage lest their finds lose value.
Collecting fluorescent minerals can be both a passion and an investment, depending on the choices made.
"In the world of collectibles, what truly shines is not just the surface, but the story every piece carries from its formation to the collector's hands."
Being savvy and informed will lead to a more fulfilling and potentially rewarding collecting experience.
Fluorescent Rocks in Nature
Fluorescent rocks are an exceptional window into geology, revealing processes that have shaped our planet over millennia. Understanding these rocks helps enthusiasts and scientists alike unlock mysteries of earth's history, one glow at a time. The way minerals emit light presents not only aesthetic allure but also a window into their geological formation and distribution across the globe. In this section, we will explore the geological formation processes that generate these luminous stones, as well as the regions known for their rich deposits of fluorescent minerals.
Geological Formation Processes
Fluorescent rocks don’t just appear out of thin air; their creation is rooted in complex geological processes. Generally, the origins of fluorescent rock can be traced back to a few key conditions: pressure, temperature, and chemical composition. These aspects work together to create minerals that have unique luminescent properties.
- Igneous Processes: Many fluorescent minerals originate in igneous environments where molten rock cools quickly, trapping various elements that contribute to fluorescence. For example, rocks like scapolite develop in this way, often emitting a striking glow under UV light.
- Metamorphic Factors: Some fluorescent luminaries, such as amethyst, form as a result of metamorphism. High pressures and elevated temperatures alter the mineral structure, sometimes incorporating trace elements that ignite fluorescence.
- Sedimentary Conditions: Fluorescent sedimentary rocks can form in environments laden with organic materials. Phosphorescent minerals can emerge during the fossilization process, where organic remains interact with mineral-rich waters, leading to the production of minerals like fluoite.
Understanding these formation processes equips collectors to better appreciate the rocks they find. Knowing their journey from molten magma to shimmering specimen enhances the connection between the collector and their finds.
Regions Rich in Fluorescent Rocks
When it comes to locating fluorescent rocks, certain regions around the globe are standout hotspots. These areas provide not just one or two, but a bonanza of minerals waiting to gleam with luminescence.
- United States: The states of Arizona and New Mexico are often celebrated for their abundance of fluorescent minerals. The rock formations in these regions exhibit vibrant qualities due to unique geological histories.
- Switzerland: Known for its breathtaking alps, Switzerland has a rich array of fluorescent calcite and other minerals. The mountainous landscape often hides luminous treasures, making it a dream for rockhounds.
- Michigan: Notably, Michigan’s Keweenaw Peninsula offers zeolite minerals that can create extraordinarily bright fluorescences. This area has become an attraction for enthusiasts hoping to discover their own glowing specimens.
- Australia: The country boasts deposits of fluorescent opals, which radiate a stunning play of color. The unique conditions in Australian soil allow for remarkable minerals to form, attracting both collectors and geologists.
The excitement of searching for fluorescent rocks in these regions often yields memorable experiences. Each outing can transform into a geological adventure as you uncover nature's hidden gems, allowing the beauty and science of fluorescent rocks to shine in your collection.
Collecting Fluorescent Rocks
Collecting fluorescent rocks is akin to unearthing the hidden treasures of the earth, revealing not just the planet's geological makeup but also fascinating stories waiting to be told. For both amateur enthusiasts and seasoned collectors, this activity offers a blend of education, adventure, and community engagement. What makes this endeavor particularly captivating is the vibrant transformation these rocks undergo under ultraviolet light, illuminating their hidden luminescence. Furthermore, collecting fluorescent rocks allows individuals to connect with nature in a profoundly engaging way, deepening one’s appreciation for the complexity of geological formations.
Essential Tools and Techniques
To embark on the journey of collecting fluorescent rocks, certain tools can significantly enhance the experience. Here are some must-haves:
- Ultraviolet (UV) Light Source: This is perhaps the most essential tool. A portable UV flashlight or lamp will let you examine the glow of the rocks in real-time.
- Rock Hammer: Ideal for breaking apart larger specimens while minimizing damage.
- Safety Goggles and Gloves: Protecting your eyes and hands is vital since some rocks may contain hazardous materials.
- Field Guide: Having a good reference book can assist in identifying fluorescent minerals.
- Sample Bags: Simple cloth or plastic bags to keep your finds safe and organized on field outings.
Understanding the techniques is just as crucial as having the right tools. One effective method involves studying known collectors’ locations or popular mining sites that are rich in these minerals. Joining local clubs or online forums such as reddit.com can yield tips about locations worth exploring. Utilizing dowsing rods or GPS devices to navigate can also enhance your prospecting experience. Don't forget to document your finds using photos and notes.
Respecting Natural Habitats
As much as the thrill of the hunt can excite one's spirit, it is equally important to recognize the responsibility that comes with collecting. Respecting natural habitats is not merely a suggestion but a necessity for the sustainability of geological resources. Unchecked collection can lead to environmental degradation, disrupting local ecosystems. Here are some practices to consider:
- Follow Local Laws: Each area has regulations concerning rock collecting; make sure you're informed and compliant.
- Limit Your Impact: Take only what you need and leave the environment as you found it. Explore areas that need cleaning up rather than those rich in biodiversity.
- Educate Yourself: Understanding the ecological significance of these areas — which often serve as homes to various plants and animals — can enhance your respect and encourage better collecting habits.
- Participate in Conservation Efforts: Seeking ways to give back, such as participating in clean-up drives or joining conservation groups, can help ensure these glorious formations are preserved for future generations.
Collecting fluorescent rocks should not be seen solely as a pastime but as an opportunity to engage with our planet responsibly, ensuring these brilliant artifacts not just shine brightly today but continue to do so for years to come.
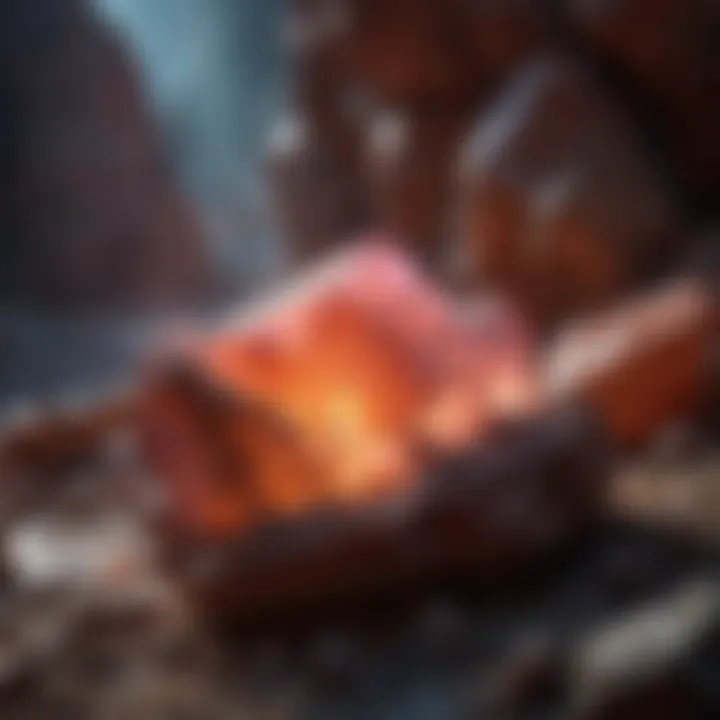

Identifying Your Finds
Recognizing the unique traits of fluorescent rocks is a significant venture for both novice and seasoned collectors. The thrill of unearthing a mineral that glows under ultraviolet light can be an unforgettable experience. Therefore, understanding how to identify these fascinating specimens not only enhances your collection but also deepens your appreciation for geology.
When you find a rock that piques your interest, the first step is to observe its visual and physical characteristics. Not all rocks exhibit fluorescence, so knowing what to look for is key to avoiding frustration.
Visual and Physical Characteristics
Fluorescent rocks can be striking to the naked eye even before exposure to UV light. One notable characteristic is their color. Many fluorescent minerals exhibit vibrant hues like green, orange, yellow, or pink when illuminated. For example, fluorite often exhibits shades of purple and green, while calcite can glow in a brilliant orange.
Here a few more points to consider when identifying these specimens:
- Texture: Observe if the rock feels smooth or rough. Some fluorescent minerals like barite might have a more crystalline appearance, while others might appear more earthy or dense.
- Weight: To an experienced collector, the heft of a rock can hint about its mineral content. For example, minerals like galena are notably heavy due to their lead content.
- Color in Daylight: Pay attention to the rock's color when it's not under UV light. This can provide clues to its mineral composition.
For clarity, it may be helpful to compile a small portfolio of common fluorescent minerals with characteristics you can easily reference during your hunting. The more you familiarize yourself with various specimens, the easier it becomes to identify new pieces.
Testing for Fluorescence
Once you've narrowed down your finds, the exciting step of testing for fluorescence begins. This is where the real fun happens as you discover whether your rock glows under a UV light source. UV lights come in different wavelengths, primarily longwave and shortwave, and each might yield different results.
Here’s a simplified process to test your finds:
- Select your UV light: The handy black light often found in party supplies can be effective, but specialized UV lamps are available that might provide better results.
- Dark Environment: Perform the test in a dark room to fully appreciate the effects. In dim lighting, even the slightest glow can be noticeable.
- Turn on your light: Point your UV flashlight at the mineral. Observe its reaction. Some minerals may glow intensely, while others might exhibit a faint glow.
- Record your findings: Whether the rock fluoresces brightly or not can help determine its value and type.
"The thrill of finding a piece that lights up is often just as exhilarating as the initial discovery in nature."
With a blend of skilled observation and scientific testing, you pave the path for building a richer collection of fluorescent rocks. Developing these skills can turn the common experience of picking up rocks into a rewarding journey that resonates with your passion for geology.
Preservation and Display
Preserving and displaying fluorescent rocks holds great significance for both collectors and enthusiasts. Proper preservation ensures that these unique specimens maintain their luminous qualities, allowing them to be enjoyed for years to come. Displaying them effectively not only showcases the beauty of each mineral but also educates onlookers about their intriguing properties.
When it comes to preservation, one must consider factors such as light exposure, temperature, and humidity. Fluorescent minerals can be sensitive to environmental changes, and neglecting these elements might lead to fading or other damages over time. Displaying these rocks in a controlled environment helps protect their integrity, maintaining both their value and aesthetic appeal.
Best Practices for Storage
Storing fluorescent rocks requires some care to ensure their longevity. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Temperature Control: Store your specimens in a cool, dry place. Fluctuations in temperature can cause physical stress or crystal growth, which may alter their appearance.
- Humidity Levels: Aim to keep the humidity in your storage area low. Excess moisture can lead to mold growth, which is detrimental to both the rocks and their display cases.
- Light Exposure: It's wise to keep these rocks out of direct sunlight when not on display. Prolonged exposure can dull their glow, compromising their beauty.
- Secure Containers: Use acid-free storage boxes or zip bags to protect your specimens. This prevents damage from dust or accidental bumps.
Keeping careful records of where your rocks were collected, and their specific properties can also add value to your collection.
Creating Effective Displays
Displaying your fluorescent rocks can be both a creative and an educational endeavor. Here are some points to consider for an impactful display:
- Utilize UV Light: Integrate UV lights to showcase the fluorescence of your rocks. Make sure to position them strategically to enhance the visibility of each specimen's glow.
- Label Clearly: Information labels can enrich your display. Include details such as the mineral's name, origin, and special features. This not only informs visitors but also adds a personal touch to your collection.
- Arrange Thoughtfully: Organize your display to create visual unity. Group similar colors or types together, allowing viewers to appreciate the variations in fluorescence across different specimens.
- Protective Cases: If using glass display cases, ensure they are UV-filtering to protect the rocks from fading while still allowing their beauty to shine.
"A vibrant display not only catches the eye but can ignite curiosity and fascination in others, leading them to explore the world of fluorescent rocks themselves."
By incorporating these practices, collectors can ensure their fluorescent rocks remain a captivating focal point in any setting, turning simple minerals into a dazzling display of nature's wonders.
The Role of Technology in Fluorescent Rock Research
In the realm of fluorescent rock research, technology has become an indispensable ally. The tools and methods developed over the years have transformed how collectors and enthusiasts explore, analyze, and appreciate these luminous gems. Gone are the days when simple UV lights and hand lenses sufficed for identification. Now, cutting-edge equipment enables a deeper understanding of not just how these rocks fluoresce, but why they do so, pushing the boundaries of both curiosity and collection.
The role of technology in this field can be categorized into several key aspects:
- Enhanced identification methods
- Improved data collection
- Broader accessibility to research and findings


The integration of technology into fluorite research is a bridge between basic geology and advanced scientific inquiry. Each step forward brings new opportunities for collectors to connect with their finds on an intellectual level.
Advancements in Equipment
Recent years have seen tremendous growth in specialized equipment designed to study fluorescent minerals. One noteworthy advancement is the development of portable fluorescence spectrometers. These compact devices allow collectors to easily analyze the wavelengths emitted by minerals in the field. The light emitted provides information not only about the mineral’s identity but also its chemical properties.
Additionally, advancements in digital imaging have made significant impacts. Techniques such as photoluminescence imaging allow for the capture of high-resolution images, revealing subtle details that the naked eye cannot discern. With such detailed imaging, nuances in crystal structure and impurities can be detected, leading to a richer understanding of mineral characteristics.
Impact of Digital Technology
Digital technology has redefined how knowledge about fluorescent rocks is shared and accessed. Online databases and platforms, like those found on Wikipedia or Reddit, provide a wealth of information that collectors previously might have spent years accumulating. These resources allow for the quick dissemination of findings, making it easier for new collectors to learn from seasoned veterans.
Furthermore, social media platforms, like Facebook, have fostered communities where collectors can share their experiences, insights, and discoveries. This global network not only enhances knowledge sharing but also encourages collaboration between enthusiasts from diverse geographical areas.
"The beauty of technology lies in its ability to connect minds and broaden horizons, bridging gaps that once felt insurmountable."
The impact is profound; research papers and findings are now accessible to a wider audience, encouraging a culture of collaboration and innovation. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the practices surrounding the study of fluorescent minerals. This forward momentum not only benefits researchers but enhances the enjoyment and appreciation for all who engage in the collecting community.
Community and Resources
Community plays a crucial role in the world of fluorescent rock collecting. For starters, enthusiasts often thrive in groups where knowledge and experiences can be shared. Being part of a community allows collectors to exchange ideas, share tips, and discuss results from their own explorations. It can also foster a sense of belonging and camaraderie among individuals who share a deep interest in geology and luminescent minerals.
Joining a collector group or community can open doors to numerous resources that may not be readily available as solo explorers. Collectors can organize field trips to known sites rich in fluorescent minerals, attend workshops, and gain firsthand knowledge from seasoned collectors. Networking opportunities abound, leading to potential partnerships for larger explorations or even research ventures. Additionally, one can tap into the vast wisdom of those who've treaded these paths before, thus avoiding common pitfalls in the collecting journey.
Furthermore, the sense of mentorship that often exists within these communities can enhance your skills in identifying, collecting, and preserving fluorescent rocks. Mentors can help newcomers navigate the intricacies of what to look for in the field and how to care for their collections. Thus, community membership is more than just joining a group—it’s about personal growth and development in rock collecting.
Joining Collector Groups
When one thinks of joining collector groups, the benefits extend far beyond simple socialization. For rock collectors, especially those interested in fluorescent rocks, these groups often serve as a treasure trove of information. It’s here that you might learn how to differentiate between similar-looking minerals or discover the latest locations where unusual specimens have been found.
Many groups convene both online and offline. Online forums, such as those found on Reddit, allow collectors from all backgrounds to pose questions, share discoveries, or seek help in identifying rocks. Facebook is another venue where numerous collector groups exist, often tailored to specific interests or local regions. These platforms enable members to post pictures and share photos of their latest finds, fostering interactive learning and collaboration.
Among the numerous benefits, attending regular meetups tends to be a highlight for many. In-person gatherings provide hands-on opportunities to explore together and learn from each other through real-world experiences. Group events also tend to include talks from experts in the field, providing fresh insights into the science behind fluorescence, as well as practical advice on collecting.
Online Resources for Learning
The digital landscape has evolved to include a multitude of resources for those interested in fluorescent rocks. These online tools can be exceptionally valuable for both new and experienced collectors seeking to expand their understanding.
One significant resource is educational websites like Britannica, which offer comprehensive articles about fluorescent minerals and their characteristics. This platform can provide foundational knowledge about the subject, making it easier for enthusiasts to engage in more specialized discussions within their communities.
In addition, platforms such as YouTube house countless videos demonstrating various techniques for collecting and identifying fluorescent rocks. These visual aids can often elucidate intricate processes that might be confusing when only read about.
Online databases and archives also serve the community well. Numerous websites compile images and data on various minerals, illustrating their properties and potential fluorescence under different lighting conditions. This not only enhances knowledge but provides a reference library to review when required.
Finally, active forums on sites like Reddit often lend a platform for discussion around recent findings, trends in collecting habits, or tips about tools and techniques—giving collectors fresh insights routinely. Engaging in these online communities can lead to a plethora of informal learning opportunities that can deepen one’s understanding of fluorescent rocks.
Pursuing knowledge in a community enriches the experience of rock collecting; it's not just about what you find but also how you connect with others who share your passion.
Closure
Fluorescent rock collecting is not merely a niche hobby; it embodies an intersection of science, history, and nature that appeals to enthusiasts and casual observers alike. More than just pretty stones glowing in the dark, these rocks tell stories of geological processes spanning millions of years. The specific elements discussed throughout this article highlight several benefits and considerations regarding this captivating field.
The Future of Fluorescent Rock Collecting
As the field of geology advances, so too does the excitement surrounding fluorescent minerals. More collectors are being drawn to this distinctive area, fueled by the discovery of new sites and technologies to facilitate studying these beautiful geological specimens. Furthermore, the diving interest in sustainable practices gives hope for the preservation of natural habitats, ensuring that generations ahead can enjoy the thrill of discovering glowing rocks.
"In every glowing rock, there's a glimpse into Earth's hidden wonders."
To expand knowledge, technology continues to evolve in ways that can support both amateur and professional collectors. For instance, handheld UV light devices have become easily accessible, making it simpler for anyone to inspect stones in their own backyards, local parks, or during traveling. As new techniques are developed to better understand these minerals’ chemical compositions, those venturing into this facet of geology will find a treasure trove of information awaiting them.
Encouragement for Continued Exploration
The world of fluorescent rocks is vast, with numerous avenues ripe for exploration. Novices and seasoned collectors alike should embrace the challenge of expanding their horizons. Visiting different regions, attending geology conferences, and participating in local rock shows can provide fresh insights and foster connections with fellow enthusiasts.
Moreover, there’s often interdisciplinary learning to be gained from branching out to related fields. Understanding aspects of mineralogy, chemistry, or even photography techniques to showcase specimens can augment one’s collecting experience. Keep an open mind and let a curiosity for science guide your collecting adventures.
In summary, the field of fluorescent rock collecting holds immense potential for those who wish to delve deeper into the complexities of this captivating subfield. By continuing to explore, educate, and connect with like-minded individuals, collectors ensure that the wonders of geology remain a vibrant part of our cultural and natural heritage.















